
The Pennsylvania System
of School Assessment
Mathematics
Item and Scoring Sampler
2015–2016
Grade 5
Pennsylvania Department of Education Bureau of Curriculum, Assessment, and Instruction—September 2015
ii
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction .............................................................1
Mathematics Reporting Categories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
General Description of Scoring Guidelines for Mathematics Open-Ended Questions.....3
Description of Sample Questions.............................................4
Mathematics Formula Sheet.................................................5
Multiple-Choice Questions ..................................................7
First Open-Ended Question ................................................40
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline .........................................42
First Open-Ended Question Responses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Second Open-Ended Question . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline .........................................56
Second Open-Ended Question Responses ....................................58
Third Open-Ended Question................................................68
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline .........................................71
Third Open-Ended Question Responses ......................................73
Fourth Open-Ended Question . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline .........................................90
Fourth Open-Ended Question Responses .....................................92
Fifth Open-Ended Question ...............................................102
Item-Specific Scoring Guideline ........................................104
Fifth Open-Ended Question Responses......................................106

1
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
INTRODUCTION
General Introduction
The Pennsylvania Department of Education provides districts and schools with tools to assist in delivering focused
instructional programs aligned with the Pennsylvania Core Standards (PCS). These tools include Academic
Standards, Assessment Anchor documents, assessment handbooks, and content-based item and scoring samplers.
This Item and Scoring Sampler is a useful tool for Pennsylvania educators in preparing local instructional programs.
It can also be useful in preparing students for the statewide assessment.
Pennsylvania Core Standards (PCS)
This sampler contains examples of test questions that are aligned to the new Pennsylvania Core Standards-based
2013 PSSA Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content. The Mathematics, Reading, and Writing PSSA transitioned to
PCS-based operational Mathematics and English Language Arts assessments starting with the spring 2015 PSSA
administration.
The 2013 PCS-aligned Assessment Anchor and Eligible Content documents are posted on this portal:
www.education.pa.gov [Hover over “K–12,” select “Assessment and Accountability,” and select
“Pennsylvania System of School Assessment (PSSA).” Then select “Assessment Anchors” from the “Other
Materials” list on the right side of the screen.]
What Is Included
This sampler contains test questions (items) that have been written to align to the Assessment Anchors that are
based on the Pennsylvania Core Standards (PCS). The test questions provide an idea of the types of items that will
appear on an operational, PCS-based PSSA. Each sample test question has been through a rigorous review process
to ensure alignment with the Assessment Anchors.
Purpose and Uses
The items in this sampler may be used as examples for creating assessment items at the classroom level, and they
may also be copied and used as part of a local instructional program.
1
Classroom teachers may find it beneficial to
have students respond to the open-ended items in this sampler. Educators can then use the sampler as a guide to
score the responses either independently or together with colleagues within a school or district.
Item Format and Scoring Guidelines
The multiple-choice (MC) items have four answer choices. Each correct response to an MC item is worth one point.
Each open-ended (OE) item is designed to take approximately ten to fifteen minutes to complete. During the
administration of the PSSA, students are given additional time as necessary to complete the test items. Each OE
item in mathematics is scored using an item-specific scoring guideline based on a 0–4 point scale. In this sampler,
every item-specific scoring guideline is combined with examples of student responses that represent each score
point to form a practical, item-specific scoring guide.
The sampler also includes the General Description of Scoring Guidelines for Mathematics Open-Ended Questions
that students will have access to during a PSSA mathematics administration. The general description of scoring
guidelines can be distributed to students for use during local assessments and can also be used by educators when
scoring local assessments.
1
1
The permission to copy and/or use these materials does not extend to commercial purposes.

2
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
Item Alignment
All PSSA items are aligned to statements and specifications included in the Assessment Anchors and Eligible
Content Aligned to the Pennsylvania Core Standards. The mathematics content, process skills, directives, and action
statements included in the PSSA mathematics questions align with the Assessment Anchor Content Standards. The
Eligible Content statements represent the limits of the content of the mathematics questions.
Testing Time and Mode of Testing Delivery for the PCS-Based PSSA
The PSSA is delivered in traditional paper-and-pencil format as well as in an online format. The estimated time to
respond to a test question is the same for both methods of test delivery. During an official testing administration,
students are given additional time as necessary to complete the test questions. The following table shows the
estimated response time for each item type.
Item Type MC OE
Estimated Response Time
(in minutes)
2 10 to 15
MATHEMATICS REPORTING CATEGORIES
The Assessment Anchors are organized into four classifications, as listed below.
` A = Numbers and Operations ` C = Geometry
` B = Algebraic Concepts ` D = Data Analysis and Probability
These four classifications are used throughout the grade levels. In addition to these classifications, there are five
Reporting Categories for each grade level. The first letter of each Reporting Category represents the classification;
the second letter represents the Domain as stated in the Common Core State Standards for Mathematics. Listed
below are the Reporting Categories for Grade 5.
` A-T = Numbers and Operations in Base Ten
` A-F = Numbers and Operations—Fractions
` B-O = Operations and Algebraic Thinking
` C-G = Geometry
` D-M = Measurement and Data
Examples of multiple-choice and open-ended items assessing these categories are included in this booklet.
3
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SCORING GUIDELINES
FOR MATHEMATICS OPEN-ENDED QUESTIONS
4 – The response demonstrates a thorough understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures
required by the task.
The response provides correct answer(s) with clear and complete mathematical procedures shown and a
correct explanation, as required by the task. Response may contain a minor “blemish” or omission in work or
explanation that does not detract from demonstrating a thorough understanding.
3 – The response demonstrates a general understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures
required by the task.
The response and explanation (as required by the task) are mostly complete and correct. The response
may have minor errors or omissions that do not detract from demonstrating a general understanding.
2 – The response demonstrates a partial understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures
required by the task.
The response is somewhat correct with partial understanding of the required mathematical concepts
and/or procedures demonstrated and/or explained. The response may contain some work that is
incomplete or unclear.
1 – The response demonstrates a minimal understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures
required by the task.
0 – The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any understanding of
the mathematical concepts and procedures required by the task for that grade level.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
4
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
DESCRIPTION OF SAMPLE QUESTIONS
The mathematics multiple-choice questions begin on page 7. Each question is preceded by the Assessment Anchor
and Eligible Content coding to which it aligns. Incorrect answer options are followed by the “rationale” which
supports the student’s response. All correct answer options are indicated by an asterisk (*).
Five open-ended questions follow the multiple-choice questions. Each open-ended question includes question-
specific scoring guidelines and examples of student responses with scores and annotations.
Since the PSSA is delivered in both paper-and-pencil and online formats, OE items of each method of test delivery
are included in this sampler. The online OE sample items are presented as screen shots in a landscape orientation
in order to best approximate the view of a computer monitor. The examples of student responses that follow the
online OE sample items are also presented as screen shots.
A calculator is permitted for use in solving questions numbered 6–50 in this sampler. Questions numbered 1–5 are
to be solved without the use of a calculator. Scratch paper may be used in solving all questions.

5
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
MATHEMATICS FORMULA SHEET
Below is a Mathematics formula sheet that will be available to students during the test. The formula sheet reflects
the mathematical approach included in the Assessment Anchors that are based on the Pennsylvania Core Standards
(PCS). The formula sheet is also available in Spanish.
Standard Conversions
Metric Conversions
Time Conversions
Rectangular Prism
1 mile (mi) = 1,760 yards (yd)
1 mile = 5,280 feet (ft)
1 yard (yd) = 3 feet (ft)
1 foot = 12 inches (in.)
1 ton (T) = 2,000 pounds (lb)
1 pound = 16 ounces (oz.)
1 gallon (gal) = 4 quarts (qt)
1 quart = 2 pints (pt)
1 pint = 2 cups (c)
1 cup = 8 fluid ounces (fl oz.)
1 kilometer (km) = 1,000 meters (m)
1 meter = 100 centimeters (cm)
1 centimeter = 10 millimeters (mm)
1 kilogram (kg) = 1,000 grams (g)
1 liter (L) = 1,000 milliliters (mL)
1 century = 10 decades
1 decade = 10 years (yr)
1 year (yr) = 12 months (mo)
1 year = 52 weeks (wk)
1 year = 365 days
1 week = 7 days
1 day = 24 hours (hr)
1 hour = 60 minutes (min)
1 minute = 60 seconds (sec)
Volume = length × width × height
V =
l × w × h
Volume = area of the base × height
V = B × h
Volume = area of the base × width
V = B × w
Volume = area of the base × length
V = B ×
l
l
w
h
Formulas and conversions that you may need to work questions on this test are
found below. You may refer back to this page at any time during the mathematics test.
2016
Grade 5

6
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
On the following pages are the mathematics questions.
• You may not use a calculator for questions 1–5. You may use a calculator for all other
questions on this test.
Directions for Multiple-Choice Questions:
Some questions will ask you to select an answer from among four choices.
For the multiple-choice questions:
• First solve the problem on scratch paper.
• Choose the correct answer and record your choice in the answer booklet.
• If none of the choices matches your answer, go back and check your work for possible errors.
• Only one of the answers provided is the correct response.
Directions for Open-Ended Questions:
Some questions will require you to write your response.
For the open-ended questions:
• These questions have more than one part. Be sure to read the directions carefully.
• You cannot receive the highest score for an open-ended question without completing all
tasks in the question. For example, if the question asks you to show your work or explain your
reasoning, be sure to show your work or explain your reasoning in the space provided.
• If the question does not ask you to show your work or explain your reasoning, you may use
the space provided, but only those parts of your response that the question specifically asks
for will be scored.
• Write your response in the appropriate location within the response box in the answer
booklet. Some answers may require graphing, plotting, labeling, drawing, or shading. If you
use scratch paper, be sure to transfer your final response and any needed work or reasoning
to the answer booklet.

7
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Questions 1–5 in this sampler are to be solved without the use of a calculator.
A-T.2.1.1
1. Multiply:270 × 30
A. 810
incorrect number of zeros
B. 6,100
does not carry 2,000 when multiplying 30 × 70
C. 6,210
3 × 2 = 6 (the first digit), 3 × 7 = 21 (second and third digits),
and includes a 0 at the end in the ones place
D. 8,100
A-T.2.1.1
2. Multiply:260 × 72
A. 2,340
260 × 7 + 260 × 2
B. 14,620
does not carry to the hundreds place when multiplying
C. 18,720
D. 23,400
260 × 70 + 260 × 20
*
*

8
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-F.1.1.1
3. Nora hiked 8
1
}
3
miles on Monday and 5
3
}
4
miles on Tuesday. What was the total number of
miles Nora hiked on Monday and Tuesday?
A. 13
1
}
12
does not carry the 1 from 13/12
B. 13
4
}
7
adds numerators and denominators
C. 14
1
}
12
D. 14
1
}
4
finds common denominator of 12 but multiplies the numerator
of 1/3 by 3 and the numerator of 3/4 by 4
A-F.2.1.2
4. Multiply:3
1
}
2
× 4
2
}
3
A. 4
converts to 3/2 and 8/3, then multiplies
B. 8
1
}
6
adds instead of multiplies
C. 12
1
}
3
multiplies whole numbers and multiplies fractions
D. 16
1
}
3
*
*

9
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-F.2.1.4
5. Divide:24 ÷
1
}
8
A.
1
}
192
inverts 24 and multiplies (1/24) x (1/8)
B.
1
}
3
inverts both 24 and 1/8 and multiplies (1/24) x 8
C. 3
multiplies 24 x (1/8)
D. 192
A calculator is permitted for use in solving questions numbered 6–50 in this sampler.
A-T.1.1
6. Martha makes the statement shown below.
When multiplying two whole numbers that end in zeros, the product always has
the exact same number of zeros at the end as the number of zeros from the end
of the two numbers combined.
For example, the product of 80 × 400 has exactly three zeros at the end since 80 ends in one
zero and 400 ends in two zeros. Which expression proves Martha’s statement is not correct?
A. 10 × 100
uses only powers of 10, but does not disprove Martha’s statement
B. 20 × 200
thinks not using powers of 10 is enough to disprove Martha’s statement
C. 30 × 400
product of 3 × 4 is greater than 10
D. 40 × 500
*
*

10
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.1.1.1
A-T.1.1.3
7. A number has an 8 in the hundredths place. The number also contains a digit whose value
is
1
}
10
the value of the 8 in the hundredths place. Which could be the expanded form of the
number?
A. (1 × 100) + (8 × 0.1) + (8 × 0.01) + (2 × 0.001)
locates hundredths correctly but uses 10 times value instead of 1/10
B. (3 × 100) + (8 × 10) + (2 × 1) + (2 × 0.1) + (8 × 0.01) + (7 × 0.001)
locates hundredths correctly but uses 100 times value instead of 1/10
C. (8 × 100) + (8 × 10) + (1 × 0.1) + (7 × 0.01) + (9 × 0.001)
uses hundreds instead of hundredths
D. (2 × 100) + (7 × 10) + (2 × 1) + (8 × 0.01) + (8 × 0.001)
A-T.1.1.2
8. In the expression shown below, a and b represent different whole numbers.
10
a
× 10
b
How many zeros must be in the product of the expression?
A. a + b
B. a × b
uses multiplication sign from expression
C. 2
number of zeros in expression as shown
D. 100
10 x 10
*
*

11
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.1.1.3
9. Lucy’s dog weighs nine and seventy-five hundredths kilograms. What is the weight, in
kilograms, of Lucy’s dog written in expanded notation?
A. 9 + 0.07 + 0.005
wrong place value for the 7 and the 5
B. 9 + 0.07 + 0.05
wrong place value for the 7
C. 9 + 0.7 + 0.005
wrong place value for the 5
D. 9 + 0.7 + 0.05
A-T.1.1.4
A-T.1.1.3
10. Which inequality correctly compares six and fifty-ninehundredths to six and
ninety-fivethousandths?
A. 6.059 < 6.95
confuses hundredths and thousandths, but compares
written decimals correctly
B. 6.059 > 6.95
confuses hundredths and thousandths, but compares
word forms of numbers correctly
C. 6.59 < 6.095
decimals written correctly but incorrect comparison
D. 6.59 > 6.095
*
*

12
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.1.1.5
A-T.2.1.3
11. Tyler’s bag of shells weighs 4.97 pounds. He finds 2 stones that weigh the same as each
other and adds them to the bag. Tyler’s bag now weighs 6.31 pounds. What is the weight of
each stone to the nearest tenth of a pound?
A. 0.6
rounds down or truncates
B. 0.7
C. 1.3
does not divide by 2 but rounds correctly
D. 2.6
multiplies by 2 and rounds down or truncates
A-T.2
12. Four friends ate together at a restaurant. The cost for each meal, without a tip, is shown below.
$11 $13 $13 $14
The total cost of the 4 meals with the tip was 1.2 times the total cost of the meals without the
tip. The friends equally shared the total cost of the meals with the tip. How much did each
friend pay?
A. $10.20
amount of tip
B. $12.75
average cost of each meal without tip
C. $13.05
adds 1.2 to the total cost of the meals without tip
D. $15.30
*
*

13
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.2.1.1
A-T.2.1.2
13. A store has 108 boxes of model cars. Each box contains 18 cars. After all the cars are
unpacked, they are arranged into 27 rows with the same number of cars in each row. How
many cars are in each row?
A. 72
B. 153
adds all numbers
C. 162
reverses multiplication and division
D. 972
subtracts 18 from 27, then multiplies 108 by result
A-F.1
14. An expression is shown below.
1
4
}
5
+ 1.25 – 2.1
The value of the expression is represented as a fraction. The numerator of the fraction is a
whole number. What is the smallest number that could be the denominator of the fraction?
A. 5
only denominator shown in given expression
B. 10
translates to mixed numbers with denominators of 10
and 100 and chooses smallest denominator
C. 20
D. 50
translates to mixed numbers 1-1/25 and 2-1/10, finds
result of 74/100, and reduces to 37/50
*
*

14
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-F.1.1
D-M.1.1.1
15. Neal uses 1
1
}
4
gallons of water and 8cups of apple cider in a recipe. How many combined
gallons of water and apple cider does Neal use in the recipe?
A. 1
1
}
6
adds 1/4 and 1/2 by adding the denominators
B. 1
1
}
3
adds 1/4 + 1/2 = (1 + 1)/(4 + 2) = 2/6 = 1/3
C. 1
3
}
4
D. 2
1
}
4
uses 8 cups = 1 gallon and then adds 1-1/4 + 1
A-F.2
16. Aubrey has a shelf full of books.
• Exactly
1
}
3
of the books on the shelf are mysteries.
• Aubrey has read 10 of the mysteries on the shelf.
• The number of mysteries Aubrey has read is greater than
1
}
5
of the number of
mysteries on the shelf and less than
1
}
4
of the number of mysteries on the shelf.
Which could be the number of books on the shelf?
A. 120
number of books on the shelf if Aubrey read exactly 1/4 of the mysteries
B. 142
within acceptable range but is not a multiple of 3
C. 147
D. 150
number of books on the shelf if Aubrey read exactly 1/5 of the mysteries
*
*

15
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-F.2.1.1
17. Kelly spends 5 hours making pizzas. Each pizza takes her
1
}
4
hour to make. When she is
finished, all of the pizzas are shared equally among 6 families. How many pizzas does each
family receive?
A.
5
}
24
multiplies instead of divides: (5 × 1/4) ÷ 6
B.
3
}
10
reverses unit fraction division and then multiplies instead of divides: (1/4 ÷ 5) × 6
C. 3
1
}
3
D. 7
1
}
2
multiplies all numbers: 5 × 1/4 × 6
A-F.2.1.2
A-F.2.1.4
18. Janet has
4
}
9
gallon of paint. She uses
1
}
8
of the paint she has to cover 3 canvases. She uses
the same amount of paint to cover each canvas. What amount of paint does Janet use to
cover each canvas?
A.
1
}
54
gallon
B.
5
}
72
gallon
subtracts 3 × 1/8 from 4/9 thinking each canvas needed 1/8 gallon
C.
1
}
6
gallon
multiplies by 3 instead of 1/3
D.
23
}
24
gallon
subtracts 1/8 from 4/9 and then multiplies by 3
*
*

16
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-F.2.1.2
A-F.2.1.1
19. Wendell has 12 cups of rice. He puts an equal amount of rice into each of 5 bowls.
Wendell eats
1
}
3
of a bowl of rice. How many cups of rice does Wendell eat?
A.
5
}
36
reverses initial division: 5/12 instead of 12/5, then multiplies 5/12 x 1/3 correctly
B.
4
}
5
C. 1
1
}
4
reverses initial division: 5/12 instead of 12/5; then multiplies by the reciprocal, 3, not 1/3
D. 7
1
}
5
correctly uses 12/5 but then multiplies by the reciprocal, 3, not 1/3
A-F.2.1.3
20. The product of
3
}
8
and any whole number is less than the whole number. Which statement
about the fraction
3
}
8
is a reason why this is true?
A. The numerator is greater than 1.
does not realize value of entire fraction is important, not just the value of the numerator
B. The denominator is greater than 1.
does not realize value of entire fraction is important, not just the value of the denominator
C. The denominator is greater than the numerator.
D. The difference between the denominator and the numerator is greater than the
numerator.
knows a comparison between the numerator and denominator is important, but does not
use the correct comparison
*
*

17
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-F.2.1.4
A-F.2.1.2
21. Paul has
1
}
2
gallon of liquid fertilizer. He puts an equal amount of the fertilizer into each of
5bottles. Paul then uses
1
}
3
of the fertilizer from one of the bottles on a flower. What fraction of
a gallon of fertilizer does Paul use on the flower?
A.
1
}
30
B.
7
}
30
correctly calculates 1/10 gallon per bottle but then subtracts 1/10 from 1/3
C.
3
}
10
correctly calculates 1/10 gallon per bottle but then divides 1/10 by 1/3
D.
5
}
6
incorrectly calculates 5/2 gallon per bottle (1/2 × 5)
*

18
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-F.2.1.4
A-F.1.1.1
22. Greg makes a pan of brownies.
• He takes
2
}
3
of the brownies to his friend’s house.
• He freezes
1
}
4
of the brownies.
• He gives the remaining brownies to his 4 sisters.
• His sisters equally share the remaining brownies.
What fraction of the pan of brownies does each sister get?
A.
1
}
48
B.
1
}
16
adds 4 to denominator instead of dividing 1/12 by 4
C.
1
}
8
subtracts 4 from denominator instead of dividing 1/12 by 4
D.
1
}
3
divides denominator by 4 instead of dividing 1/12 by 4
B-O.1.1.1
B-O.2.1
23. Mark makes a pattern that starts with 5 and uses the rule “subtract 1, and then multiply by 3.”
Which expression can be used to find the thirdnumber in Mark’s pattern?
A. 5 – 1 × 3 – 1 × 3
does not use any parentheses and evaluates the expession from left to right
B. 3(5 – 1) + 3(5 – 1)
writes an expression for the second number and then repeats that expression
C. 3[3(5) – 1]
multiplies 5 and 3 before subtracting 1, and omits a subtraction step
D. 3[3(5 – 1) – 1]
*
*

19
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.1.1.2
24. Which expression has half the value of 2 + 898 × 950?
A. 1 + 449 × 475
takes half of each number
B. 1 + 898 × 475
C. 2 + 449 × 475
takes half of both 898 and 950
D. 2 + 898 × 475
takes half of 950 but not half of 2
B-O.1.1.2
B-O.1.1.1
25. All the students in a class are sitting at tables.
• There are 6 round tables, and 3 boys and 4 girls are sitting at each round table.
• There are 7square tables, and 5boys and 3girls are sitting at each square table.
• Ms. Martin gives each student in the class 2 books.
Which expression can be used to find the total number of books Ms. Martin gives to the
students?
A. 2 (6 + 3 + 4 + 7 + 5 + 3)
adds all the numbers and multiplies by number of books
B. 6 (3 + 4) + 7 (5 + 3) + 2
adds number of books per student instead of multiplying
C. 2 [6 (3 + 4) + 7 (5 + 3)]
D. 6 [(3 + 4) + 2] + 7 [(5 + 3) + 2]
adds 2 books per student to number of students
*
*

20
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2
26. Linda has a jar that contains 6 coins. She adds coins to the jar each day for 5 days. The
pattern below shows the number of coins in Linda’s jar at the end of each of the 5 days.
13 20 27 34 41
Nancy also has a jar containing 6 coins. She adds twice as many coins to her jar each day as
Linda does for each of the 5 days. What is the total number of coins in Linda’s and Nancy’s
jars at the end of the 5 days?
A. 103
thinks there are 6 coins in Nancy’s jar after day 1
B. 111
forgets to add Nancy’s 6 initial coins
C. 117
D. 123
calculates Nancy’s coins by doubling Linda’s coins
*

21
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2.1
A-F.1.1.1
27. A chef bakes a turkey in one oven and a cake in another oven. The turkey and the cake start
baking at the same time. The table below shows the amount the turkey and the cake are
baked based on the amount of baking time, in minutes.
Amount Baked
BakingTime
(minutes)
5 10 15 20
Turkey
1
}
24
1
}
12
1
}
8
1
}
6
Cake
1
}
6
1
}
3
1
}
2
2
}
3
The patterns continue. Which statement best describes the relationship between the baking
time for the turkey and the baking time for thecake?
A. The turkey bakes
1
}
6
as fast as the cake.
incorrectly adds 1/6 + 1/6
B. The turkey bakes
1
}
4
as fast as the cake.
C. The turkey bakes
1
}
3
as fast as the cake.
thinks 2/3 is 1/3 more than 1/6
D. The turkey bakes
1
}
2
as fast as the cake.
compares numerators and denominators of 1/6 and 2/3
*

22
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2.1.1
28. Daniel and Jessica each make a pattern.
• Daniel’s pattern starts with 12 and uses the rule subtract 6, then multiply by 3.
• Jessica’s pattern starts with 8 and uses the rule multiply by 2, then add2.
Which pair of patterns shows Daniel’s and Jessica’s patterns?
A. Daniel’s pattern:12,18,36,90,252
Jessica’s pattern:8,20,44,92,188
Daniel’s pattern is correct, but Jessica’s pattern has
operations reversed, adds2, then multiplies by 2
B. Daniel’s pattern:12,36,108,324,972
Jessica’s pattern:8,16, 32, 64,128
only multiplies, does not add or subtract
C. Daniel’s pattern:12,18,36,90,252
Jessica’s pattern:8,18,38,78,158
*
D. Daniel’s pattern:12,30,84,246,732
Jessica’s pattern:8,18,38, 78,158
Jessica’s pattern is correct, but Daniel’s pattern has
operations reversed, multiplies by 3, then subtracts 6

23
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2.1.2
29. John and Megan each make a pattern. Each pattern starts with the number 1. The first
fiveterms in each pattern are shown below.
John’s pattern: 1,4, 7,10,13
Megan’s pattern: 1,8,15,22,29
The patterns continue. Which statement about the relationship between the corresponding
terms in the patterns is true?
A. Each term in Megan’s pattern is 7 more than the corresponding term in John’s pattern.
the terms in Megan’s pattern increase by 7
B. Each term in Megan’s pattern is less than double the corresponding term in John’s
pattern.
only true for 1st terms, and the opposite is true for terms 3 and later
C. The difference between any term in Megan’s pattern and the corresponding term in
John’s pattern is always 3.
the difference between the terms in John’s pattern is 3
D. The difference between any term in Megan’s pattern and the corresponding term in
John’s pattern is always a multiple of 4.
*

24
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1
30. Two vertices of a right triangle are located at (2, 1) and (2, 4) on a coordinate grid. The
location of the third vertex of the triangle can be described by an ordered pair in which the
whole number x-coordinate is less than the whole number y-coordinate. What is the greatest
number of ordered pairs that could describe the location of the third vertex of the triangle?
A. 1
thinks there is only one possible location of the third vertex
B. 2
does not include ordered pairs located on y-axis
C. 4
D. 6
adds the 4 possible third vertices to the 2 given vertices
C-G.1.1
31. Selena is using a coordinate grid to graph information about the last few baseball games in
which she pitched.
• The x-coordinate of each point she graphs is the number of runs she allowed.
• The y-coordinate of each point she graphs is the number of strikeouts she recorded.
Which statement about Selena’s graph is true?
A. A point other than the origin graphed on the x-axis means Selena allowed no runs.
confuses axes labels
B. A point graphed at (2, 3) means Selena allowed 3 runs and recorded 2 strikeouts.
reverses coordinates
C. A point other than the origin graphed on the y-axis means Selena recorded at least
one strikeout.
D. A point graphed at (3, 4) means Selena allowed 1 more run than the number of strikeouts
recorded.
reverses coordinates
*
*
25
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.1
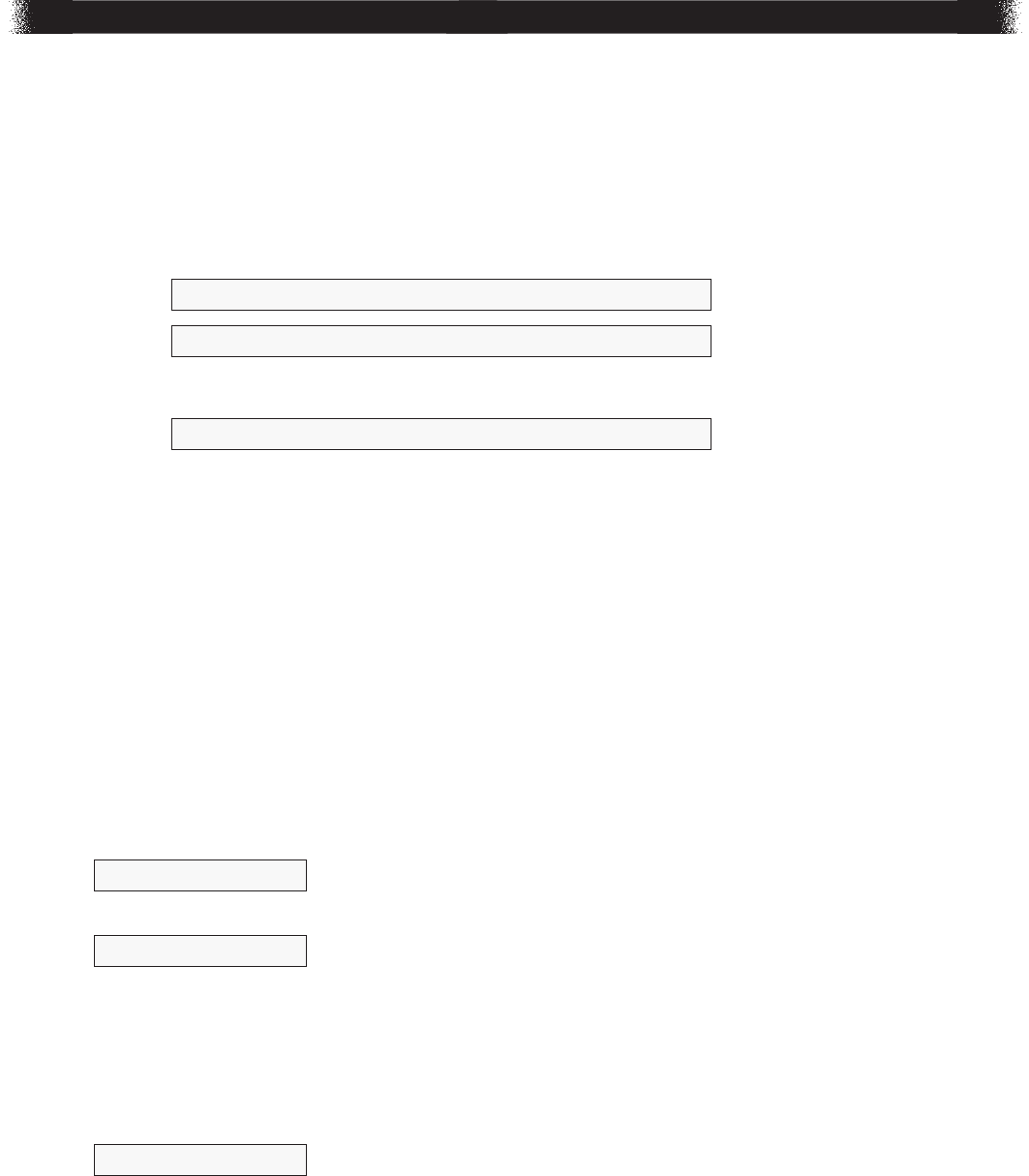
32. Zach creates a map of his neighborhood on a coordinate grid as shownbelow.
Zach’s Neighborhood
y
x
bank
park
zoo
school
0
5
5
Which location is on the x-axis but not on the y-axis of Zach’s map?
A. bank
selects point that is on both x- and y-axes
B. park
selects point that is on neither axis
C. school
confuses the axes
D. zoo
*

26
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2
33. The locations of four buildings in a town can be shown on a coordinate grid. The ordered pairs
below describe the locations of the buildings.
• movie theater: (4, 6)
• city hall: (1, 3)
• post office: (4, 1)
• market: (5, 3)
Harriet is standing closer to the market than to any of the other buildings. Which ordered pair
could describe the location at which Harriet is standing?
A. (3, 3)
same y-coordinate as market, but equidistant from city hall and market
B. (4, 3)
C. (5, 1)
same x-coordinate as market, but closest to post office
D. (5, 6)
same x-coordinate as market, but closest to movie theater
*

27
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2
34. A garage has a rectangular floor. The fourpoints graphed on the coordinate grid below
represent the locations of the fourcorners of the floor.
y
x
246810
H
J
K
L
103579
2
4
6
8
10
1
3
5
7
9
The opening for the garage door can be represented by a line segment. Each point on the
line segment has an x-coordinate of 10. The opening for the garage door lies between which
corners of the floor?
A. H and J
confuses x-coordinates and y-coordinates
B. J and K
C. K and L
confuses x-coordinate and y-coordinate and chooses ordered pairs
that have the same y-coordinate, but one that is 2 rather than 10
D. L and H
identifies points whose ordered pairs have same x-coordinate,
but one that is 2 rather than 10 (opposite wall)
*

28
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2
35. The coordinate grid below shows the location of a school library.
y
x
246810103579
2
4
6
8
10
1
3
5
7
9
school
library
N
W
E
S
The school office is located at the origin of the coordinate grid. Which describes a path that
could be followed to walk from the school library to the school office?
A. walk 2 units north, then 3 units west
misidentifies origin as (0, 11)
B. walk 3 units west, then 9 units south
C. walk 8 units east, then 2 units north
misidentifies origin as (11, 11)
D. walk 9 units north, then 3 units east
describes office to library
*

29
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2
36. The graph below shows the number of cans of green paint a store had on a shelf during a
7-day period.
y
x
2461035
Day
Green Paint on Shelf
Number of Cans of Paint
78
2
4
6
8
1
3
5
7
Based on the graph, which statement about the point graphed on the x-axis must be true?
A. The store sold 3 cans of green paint on day 3.
not enough information to determine from graph
B. There were 8 cans of green paint on the shelf on day 8.
not enough information to determine from graph
C. There were 0 cans of green paint on the shelf on day 3.
D. The store had 8 cans of green paint on the shelf at the start of the 7-day period.
interprets point graphed on y-axis
*
30
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.2
37. Two sides of a polygon are parallel and have the same length. Which statement about the
polygon must be true?
A. The polygon has exactly 3 sides.
never true
B. The polygon has exactly 4 sides.
sometimes true
C. The polygon has at least 4 sides.
D. The polygon has an even number of sides.
sometimes true
*

31
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.2.1.1
C-G.1.1.2
38. The coordinate grid below has three points plotted.
246810357
y
x
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Which point could also be plotted on the grid so that the four points form the vertices of a
parallelogram, but not a rhombus?
A. (2, 1)
B. (2, 6)
makes a trapezoid, not a parallelogram
C. (4, 5)
makes a rhombus
D. (6, 5)
makes a kite (i.e., pairs of adjacent sides are congruent), not a parallelogram
*

32
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
D-M.1.1.1
D-M.2.1.2
39. The bar graph below shows the heights, in centimeters (cm), of fourvases.
Vase Height
Vase
Height (cm)
red green blue orange
16
18
20
22
15
17
19
21
0
Based on the bar graph, what is the height, in millimeters (mm), of the vase with the greatest
height?
A. 2.1 mm
reads graph correctly but then divides by 10
B. 21.0 mm
reads graph correctly but does not convert to mm
C. 210 mm
D. 2,100 mm
reads graph correctly but multiplies by 100 instead of 10
*

33
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
D-M.2.1
40. Kenny made the pictograph below to show the number of DVDs a library purchased in each
of three months.
Key:
= 30 DVDs
DVDs Purchased Each Month
Number of DVDs
Month
January
February
March
Which statement explains why there must be an error in Kenny’s pictograph?
A. The pictograph shows the library purchased 1
1
}
2
DVDs in January.
does not use the key
B. The pictograph shows the library purchased 30
1
}
2
DVDs in January.
does not correctly interpret the half-DVD symbol
C. The pictograph shows the library purchased no DVDs in February.
assusmes each row has to have some icons in it
D. The pictograph shows the library purchased 97
1
}
2
DVDs in March.
*
34
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
D-M.2.1.1
D-M.1.1.1
41. Frankie measures and records the lengths, in feet, of nine worms. The line plot below shows
the information she records.
Worm Lengths
Length (feet)
1
8
×
×
××
×
×
×
××
1
4
3
8
1
2
5
8
3
4
7
8
Based on the line plot, what is the difference between the lengths, in inches, of the longest
worm and the shortest worm?
A. 4
1
}
2
inches
subtracts lengths of both shortest worms from longest: 7/8 – (1/4 + 1/4)
B. 7
1
}
2
inches
C. 9inches
uses greatest and least lengths shown on plot: 7/8 – 1/8
D. 18inches
subtracts numerators and denominators
*

35
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
D-M.2.1.2
D-M.1.1.1
42. The pictograph below shows the number of gallons of lemonade served each day at a
carnival.
Lemonade Served at the Carnival
Day Number of Gallons
Monday
Tuesday
Wednesday
Thursday
Key:
= 1 gallon
How many quarts of lemonade were served on Thursday?
A. 16 quarts
does not include half symbol
B. 17 quarts
counts half symbol as 1 more quart
C. 18 quarts
D. 20 quarts
interprets half symbol as a whole gallon
*

36
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
D-M.2.1.2
D-M.1.1.1
43. The bar graph below shows the annual rainfalls, in inches, of four cities.
Annual Rainfall
City
Rainfall (inches)
60
54
48
42
36
30
24
18
12
6
0
Oakville Mapleton
Pineview
Elmhurst
What is the difference, in feet, of the rainfalls of the city with the greatest rainfall and the city
with the least rainfall?
A. 2 feet
difference between first and last columns
B. 3 feet
C. 7 feet
the sum of the greatest and least rainfalls
D. 36 feet
does not convert from inches to feet
*

37
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
D-M.3.1.1
D-M.1.1.1
44. A fish tank is in the shape of a rectangular prism. The dimensions of the tank are shown in the
picture below.
84 in.
24 in.
48 in.
What is the volume of the tank in cubic feet?
A. 13 cubic feet
converts correctly but adds dimensions
B. 56 cubic feet
C. 672 cubic feet
correctly calculates volume in cubic inches, then divides by 144
D. 8,064 cubic feet
correctly calculates volume in cubic inches, then divides by 12
*

38
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
D-M.3.1.2
45. The object pictured below is made from two rectangular prisms.
8 in.
10 in.
50 in.
6 in.
30 in.
Which expression can be used to find the total volume, in cubic inches, of the object?
A. (8 × 10 × 30) + (50 × 10 × 6)
B. (8 × 10 × 30) + (50 × 8 × 6)
uses 8 as the third dimension of the vertical prism
C. (8 × 10 × 30) + (50 × 6)
does not account for the third dimension of the
vertical prism
D. (8 × 10 × 30 × 50 × 6)
multiplies all given numbers
*

39
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
THIS PAGE IS
INTENTIONALLY BLANK.
40
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
FIRST OPEN-ENDED QUESTION
A-T.1.1.2
A-T.1.1.3
46. Greg and Holly compete in a track meet.
Greg ran the 800-meter dash in 19,265 ÷ 10
2
seconds.
A. Write Greg’s time for the 800-meter dash, in seconds, in standard form. Explain
how you determined the correct placement of the decimal point.
Go to the next page to finish question 46.

41
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
46. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Holly ran the 200-meter dash in 26.43 seconds. Greg ran the 200-meter dash in
26.425 seconds. Holly makes the statement shown below.
I ran the 200-meter dash in less time than
Greg did because 43 is less than425.
B. Explain the error in Holly’s statement. As part of your explanation, find the
correct difference, in seconds, between the twotimes.

42
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
ITEM-SPECIFIC SCORING GUIDELINE
Question #46
Grade 5
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
M05.A-T.1—Understand the place-value system.
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
M05.A-T.1.1—Demonstrate understanding of place-value of whole numbers and decimals, and compare
quantities or magnitudes of numbers.
Scoring Guide:
Score In this item, the student –
4
Demonstrates a thorough understanding of the place-value system by correctly solving
problems and clearly explaining procedures.
3
Demonstrates a general understanding of the place-value system by correctly solving
problems and clearly explaining procedures with only minor errors or omissions.
2
Demonstrates a partial understanding of the place-value system by correctly performing a
significant portion of the required task.
1 Demonstrates minimal understanding of the place-value system.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Non-
Scorables
B – Blank
R – Refusal
K – Off task/topic
F – Foreign language
U – Illegible
Top Scoring Student Response And Training Notes:
Score Description
4 Student earns 4 points.
3 Student earns 3.0 – 3.5 points.
2 Student earns 2.0 – 2.5 points.
1
Student earns 0.5 – 1.5 points.
OR
Student demonstrates minimal understanding of the place-value system.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or concept
being measured.

43
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question #46
Top Scoring Response:
Part A Answer
What? Why?
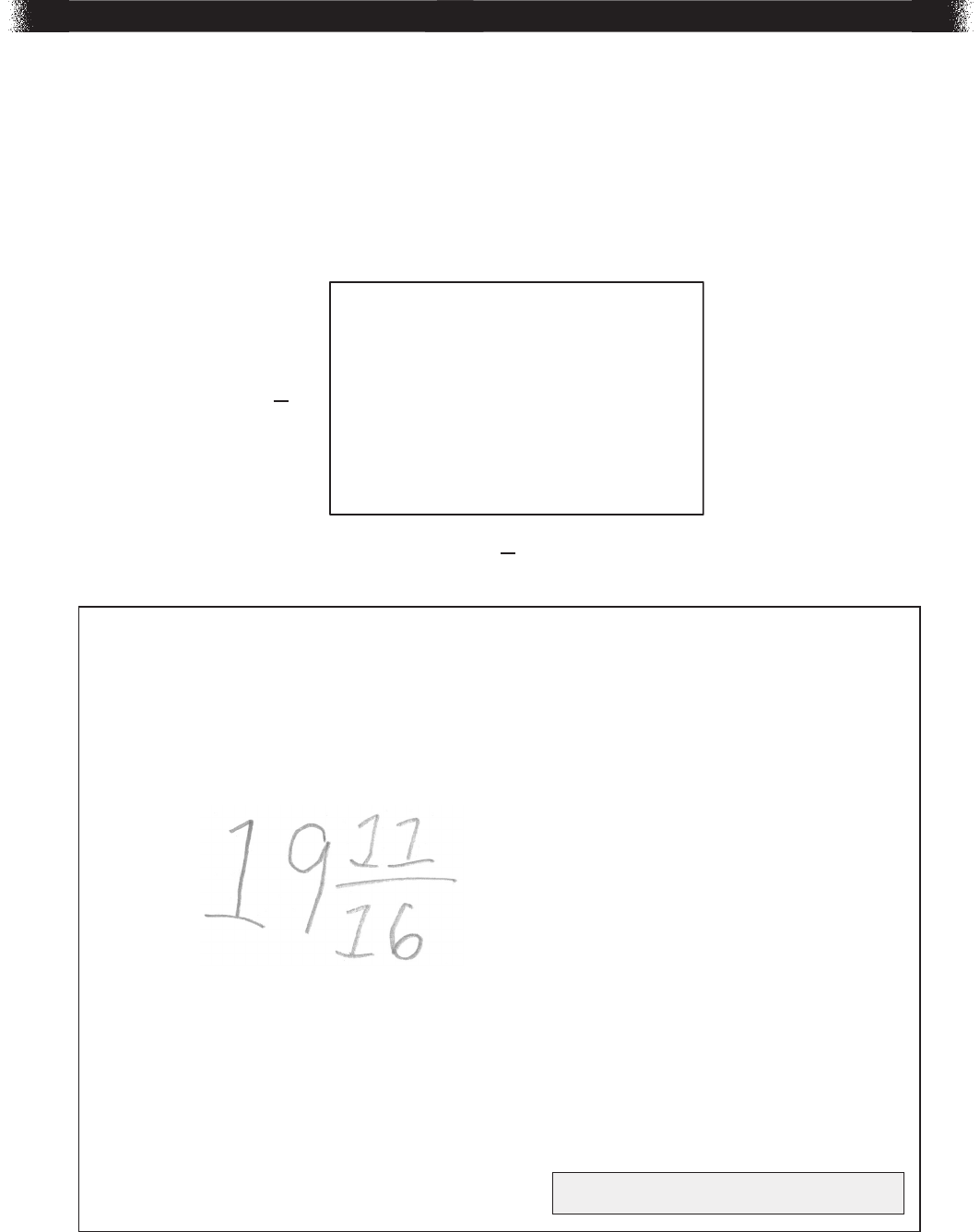
192.65 (seconds)
Sample Explanation:
Since the number 19,265 is being divided by 10
2
the actual number is smaller
than 19,265, so I need to move the decimal point to the left. The exponent 2
tells me I need to move the decimal point 2 places. So the time in standard
form is 192.65 seconds.
OR equivalent
(2 score points)
1 point for correct answer
1 point for correct and complete explanation
OR ½ point for correct but incomplete explanation
Part B Answer
What? Why?
0.005 (second) Sample Explanation:
Holly did not recognize that she is comparing tenths, hundredths, and
thousandths rather than tens and hundreds. 0.43 is more than 0.425
because
43
}
100
=
430
}
1,000
is more than
425
}
1,000
.
OR equivalent
(2 score points)
1 point for correct answer
1 point for correct and complete explanation
OR ½ point for correct but incomplete explanation

44
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
FIRST OPEN-ENDED QUESTION RESPONSES
A-T.1.1.2
A-T.1.1.3 Response Score: 4
46. Greg and Holly compete in a track meet.
Greg ran the 800-meter dash in 19,265 ÷ 10
2
seconds.
A. Write Greg’s time for the 800-meter dash, in seconds, in standard form. Explain
how you determined the correct placement of the decimal point.
Go to the next page to finish question 46.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given a complete explanation.

45
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
46. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Holly ran the 200-meter dash in 26.43 seconds. Greg ran the 200-meter dash in
26.425 seconds. Holly makes the statement shown below.
I ran the 200-meter dash in less time than
Greg did because 43 is less than425.
B. Explain the error in Holly’s statement. As part of your explanation, find the
correct difference, in seconds, between the twotimes.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given a complete explanation.

46
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.1.1.2
A-T.1.1.3 Response Score: 3
46. Greg and Holly compete in a track meet.
Greg ran the 800-meter dash in 19,265 ÷ 10
2
seconds.
A. Write Greg’s time for the 800-meter dash, in seconds, in standard form. Explain
how you determined the correct placement of the decimal point.
Go to the next page to finish question 46.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given a correct but incomplete explanation.

47
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
46. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Holly ran the 200-meter dash in 26.43 seconds. Greg ran the 200-meter dash in
26.425 seconds. Holly makes the statement shown below.
I ran the 200-meter dash in less time than
Greg did because 43 is less than425.
B. Explain the error in Holly’s statement. As part of your explanation, find the
correct difference, in seconds, between the twotimes.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given a correct but incomplete explanation.

48
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.1.1.2
A-T.1.1.3 Response Score: 2
46. Greg and Holly compete in a track meet.
Greg ran the 800-meter dash in 19,265 ÷ 10
2
seconds.
A. Write Greg’s time for the 800-meter dash, in seconds, in standard form. Explain
how you determined the correct placement of the decimal point.
Go to the next page to finish question 46.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given a complete explanation.

49
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
46. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Holly ran the 200-meter dash in 26.43 seconds. Greg ran the 200-meter dash in
26.425 seconds. Holly makes the statement shown below.
I ran the 200-meter dash in less time than
Greg did because 43 is less than425.
B. Explain the error in Holly’s statement. As part of your explanation, find the
correct difference, in seconds, between the twotimes.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

50
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.1.1.2
A-T.1.1.3 Response Score: 1
46. Greg and Holly compete in a track meet.
Greg ran the 800-meter dash in 19,265 ÷ 10
2
seconds.
A. Write Greg’s time for the 800-meter dash, in seconds, in standard form. Explain
how you determined the correct placement of the decimal point.
Go to the next page to finish question 46.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

51
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
46. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Holly ran the 200-meter dash in 26.43 seconds. Greg ran the 200-meter dash in
26.425 seconds. Holly makes the statement shown below.
I ran the 200-meter dash in less time than
Greg did because 43 is less than425.
B. Explain the error in Holly’s statement. As part of your explanation, find the
correct difference, in seconds, between the twotimes.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

52
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
A-T.1.1.2
A-T.1.1.3 Response Score: 0
46. Greg and Holly compete in a track meet.
Greg ran the 800-meter dash in 19,265 ÷ 10
2
seconds.
A. Write Greg’s time for the 800-meter dash, in seconds, in standard form. Explain
how you determined the correct placement of the decimal point.
Go to the next page to finish question 46.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

53
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
46. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
Holly ran the 200-meter dash in 26.43 seconds. Greg ran the 200-meter dash in
26.425 seconds. Holly makes the statement shown below.
I ran the 200-meter dash in less time than
Greg did because 43 is less than425.
B. Explain the error in Holly’s statement. As part of your explanation, find the
correct difference, in seconds, between the twotimes.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

54
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
SECOND OPEN-ENDED QUESTION
A-F.1
47. Pamela made a metal plate in the shape of a rectangle. The metal plate is represented
in the diagram below.
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
A. What is the area, in square inches, of the metal plate?
(Hint: Area = length × width)
Go to the next page to finish question 47.

55
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Pamela cut an opening in the metal plate in the shape of a rectangle as
represented below.
opening
width
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
1 in.
1
4
2 in.
3
8
B. What is the width, in inches, of the opening? Show or explain all your work.
Pamela calculates that the area of the opening is 9 square inches, but her
calculation is incorrect.
C. Explain why Pamela’s calculation must be incorrect.
(Hint: Area = length × width)
47. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.

56
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
ITEM-SPECIFIC SCORING GUIDELINE
Question #47
Grade 5
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
M05.A-F.1—Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions.
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
M05.A-F.1.1—Solve addition and subtraction problems involving fractions (straight computation or word
problems).
M05.A-F.2.1—Solve multiplication and division problems involving fractions and whole numbers (straight
computation or word problems).
Scoring Guide:
Score In this item, the student –
4
Demonstrates a thorough understanding of how to use equivalent fractions as a strategy to
add and subtract fractions by correctly solving problems and clearly explaining procedures.
3
Demonstrates a general understanding of how to use equivalent fractions as a strategy to
add and subtract fractions by correctly solving problems and clearly explaining procedures
with only minor errors or omissions.
2
Demonstrates a partial understanding of how to use equivalent fractions as a strategy to
add and subtract fractions by correctly performing a significant portion of the required task.
1
Demonstrates minimal understanding of how to use equivalent fractions as a strategy to
add and subtract fractions.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Non-
Scorables
B – Blank
R – Refusal
K – Off task/topic
F – Foreign language
U – Illegible
Top Scoring Student Response And Training Notes:
Score Description
4 Student earns 4 points.
3 Student earns 3.0 – 3.5 points.
2 Student earns 2.0 – 2.5 points.
1
Student earns 0.5 – 1.5 points.
OR
Student demonstrates minimal understanding of how to use equivalent fractions as a
strategy to add and subtract fractions.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or concept
being measured.

57
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question #47
Top Scoring Response:
Part A Answer
What? Why?
19
11
}
16
(square inches)
(1 score point)
1 point for correct answer
Part B Answer
What? Why?
2 (inches)
Sample Work:
5
5
}
8
– 1
1
}
4
– 2
3
}
8
= 2
OR
Sample Explanation:
I subtracted 1
1
}
4
and 2
3
}
8
from 5
5
}
8
to get 2inches for the width of the hole.
(2 score points)
1 point for correct answer
1 point for complete support
OR ½ point for correct but incomplete support
Part C Answer
What? Why?
Sample Explanation:
Since the area of the hole is the product of the width and the length, I can divide
the area by the width to find the length, 9 ÷ 2 = 4
1
}
2
. That means the hole would be
4
1
}
2
inches in length. However, the width of the entire metal plate is only 3
1
}
2
inches,
so Pamela’s calculation must be incorrect.
(1 score point)
1 point for complete explanation
OR ½ point for correct but incomplete explanation
58
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
47. Pamela made a metal plate in the shape of a rectangle. The metal plate is represented
in the diagram below.
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
A. What is the area, in square inches, of the metal plate?
(Hint: Area = length × width)
Go to the next page to finish question 47.
SECOND OPEN-ENDED QUESTION RESPONSES
A-F.1 Response Score: 4
The student has given a correct answer.

59
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Pamela cut an opening in the metal plate in the shape of a rectangle as
represented below.
opening
width
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
1 in.
1
4
2 in.
3
8
B. What is the width, in inches, of the opening? Show or explain all your work.
Pamela calculates that the area of the opening is 9 square inches, but her
calculation is incorrect.
C. Explain why Pamela’s calculation must be incorrect.
(Hint: Area = length × width)
47. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given a complete explanation.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has shown complete support.

60
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
47. Pamela made a metal plate in the shape of a rectangle. The metal plate is represented
in the diagram below.
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
A. What is the area, in square inches, of the metal plate?
(Hint: Area = length × width)
Go to the next page to finish question 47.
A-F.1 Response Score: 3
The student has given a correct answer.

61
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Pamela cut an opening in the metal plate in the shape of a rectangle as
represented below.
opening
width
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
1 in.
1
4
2 in.
3
8
B. What is the width, in inches, of the opening? Show or explain all your work.
Pamela calculates that the area of the opening is 9 square inches, but her
calculation is incorrect.
C. Explain why Pamela’s calculation must be incorrect.
(Hint: Area = length × width)
47. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has shown complete support.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

62
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
47. Pamela made a metal plate in the shape of a rectangle. The metal plate is represented
in the diagram below.
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
A. What is the area, in square inches, of the metal plate?
(Hint: Area = length × width)
Go to the next page to finish question 47.
A-F.1 Response Score: 2
The student has given an incorrect answer.

63
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Pamela cut an opening in the metal plate in the shape of a rectangle as
represented below.
opening
width
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
1 in.
1
4
2 in.
3
8
B. What is the width, in inches, of the opening? Show or explain all your work.
Pamela calculates that the area of the opening is 9 square inches, but her
calculation is incorrect.
C. Explain why Pamela’s calculation must be incorrect.
(Hint: Area = length × width)
47. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has shown complete support.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

64
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
47. Pamela made a metal plate in the shape of a rectangle. The metal plate is represented
in the diagram below.
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
A. What is the area, in square inches, of the metal plate?
(Hint: Area = length × width)
Go to the next page to finish question 47.
A-F.1 Response Score: 1
The student has given a correct answer.

65
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Pamela cut an opening in the metal plate in the shape of a rectangle as
represented below.
opening
width
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
1 in.
1
4
2 in.
3
8
B. What is the width, in inches, of the opening? Show or explain all your work.
Pamela calculates that the area of the opening is 9 square inches, but her
calculation is incorrect.
C. Explain why Pamela’s calculation must be incorrect.
(Hint: Area = length × width)
47. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has shown incorrect support.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

66
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
47. Pamela made a metal plate in the shape of a rectangle. The metal plate is represented
in the diagram below.
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
A. What is the area, in square inches, of the metal plate?
(Hint: Area = length × width)
Go to the next page to finish question 47.
A-F.1 Response Score: 0
The student has given an incorrect answer.

67
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Pamela cut an opening in the metal plate in the shape of a rectangle as
represented below.
opening
width
Metal Plate
3
in.
1
2
5 in.
5
8
1 in.
1
4
2 in.
3
8
B. What is the width, in inches, of the opening? Show or explain all your work.
Pamela calculates that the area of the opening is 9 square inches, but her
calculation is incorrect.
C. Explain why Pamela’s calculation must be incorrect.
(Hint: Area = length × width)
47. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has shown incorrect support.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

68
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
THIRD OPEN-ENDED QUESTION
B-O.2
Question 48

69
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48

70
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48

71
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
ITEM-SPECIFIC SCORING GUIDELINE
Question #48
Grade 5
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
M05.B-O.2—Analyze patterns and relationships.
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
M05.B-O.2.1—Create, extend, and analyze patterns.
Scoring Guide:
Score In this item, the student –
4
Demonstrates a thorough understanding of how to analyze patterns and relationships by
correctly solving problems and clearly explaining procedures.
3
Demonstrates a general understanding of how to analyze patterns and relationships by
correctly solving problems and clearly explaining procedures with only minor errors or
omissions.
2
Demonstrates a partial understanding of how to analyze patterns and relationships by
correctly performing a significant portion of the required task.
1 Demonstrates minimal understanding of how to analyze patterns and relationships.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Non-
Scorables
B – Blank
R – Refusal
K – Off task/topic
F – Foreign language
U – Illegible
Top Scoring Student Response And Training Notes:
Score Description
4 Student earns 4 points.
3 Student earns 3.0 – 3.5 points.
2 Student earns 2.0 – 2.5 points.
1
Student earns 0.5 – 1.5 points.
OR
Student demonstrates minimal understanding of how to analyze patterns and relationships.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or concept
being measured.

72
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question #48
Top Scoring Response:
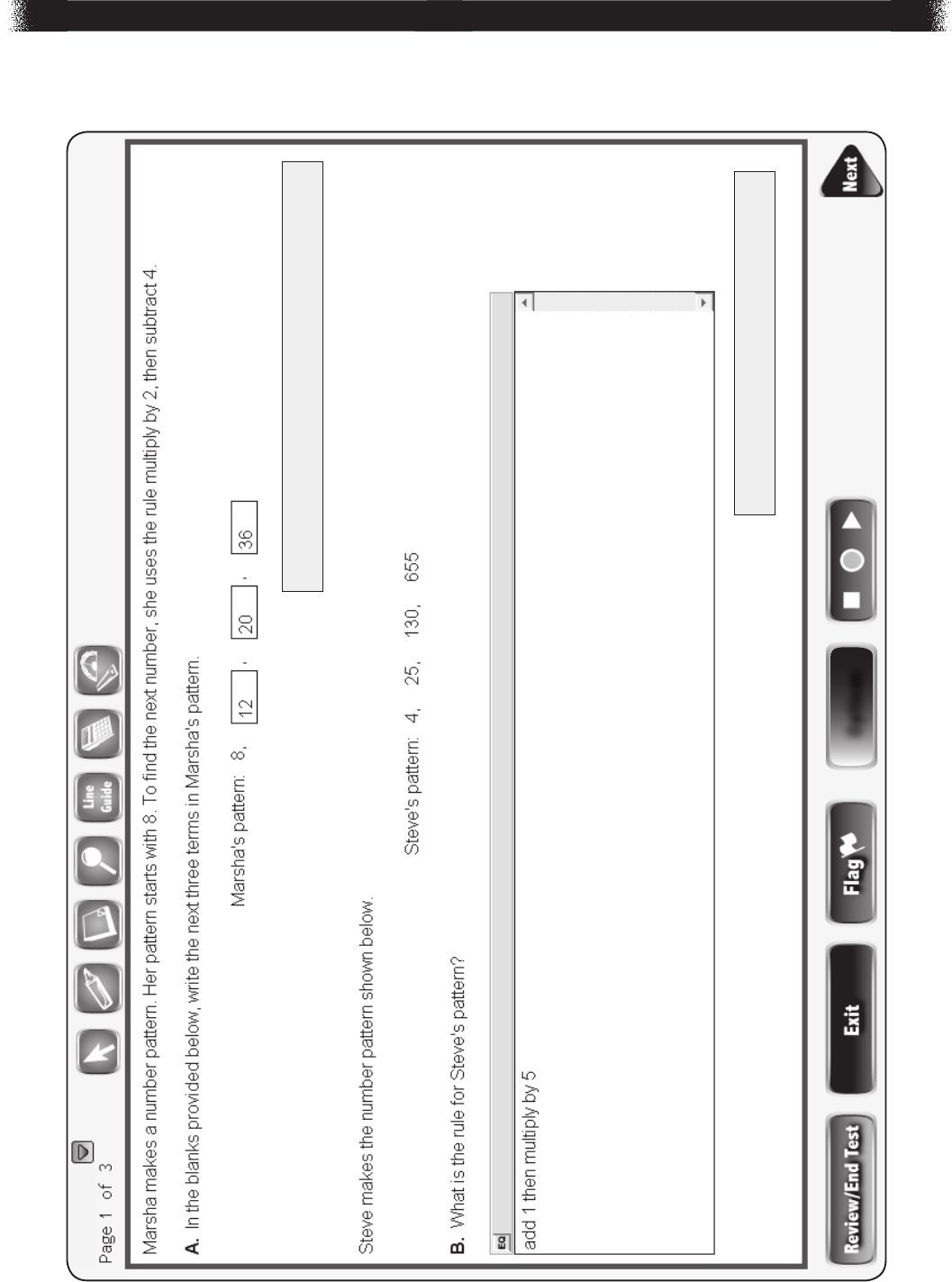
Part A Answer
What? Why?
8, 12 , 20 , 36
(1 score point)
1 point for all 3 correct answers
Part B Answer
What? Why?
add 1, then multiply by 5
OR
multiply by 5, then add 5
(1 score point)
1 point for correct answer
Part C Answer
What? Why?
Sample Explanation:
The sum of the terms in the patterns forms a new pattern. This pattern begins with
7 + 7 = 14, which is a multiple of 7 (7 × 2). Since the rule for Brenda’s pattern is “add
3” and the rule for Javier’s pattern is “add 4”, the rule for the sum pattern is “add7”.
Since the first term is a multiple of 7 and the rule is “add 7”, the sum of any term in
Brenda’s pattern and the corresponding term in Javier’s pattern will always be a
multiple of 7.
(1 score point)
1 point for complete explanation
Part D Answer
What? Why?
Answers may vary. First term must start with 21. The rule for the patterns must be
+5 OR +12 OR +19 OR +26 OR …
OR
–2 OR –9 OR –16 OR –23 OR …
Sample answers:
Dan’s possible pattern: 21, 19, 17 [uses a –2 rule]
OR
Dan’s possible pattern: 21, 40, 59 [uses a + 19 rule]
(1 score point)
1 point for correct answer

73
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
THIRD OPEN-ENDED QUESTION RESPONSES
B-O.2 Response Score: 4
Question 48
The student has given all correct answers.
The student has given a correct answer.

74
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given a complete explanation.

75
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given a correct answer.

76
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2 Response Score: 3
Question 48
The student has given all correct answers.
The student has given a correct answer.

77
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given an insufficient explanation.

78
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given a correct answer.
79
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2 Response Score: 2
Options
Question 48
The student has given all correct answers.
The student has given a correct answer.

80
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

81
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect answer.

82
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2 Response Score: 1
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given all correct answers.

83
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

84
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect answer.

85
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
B-O.2 Response Score: 0
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given an incorrect answer.

86
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

87
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 48
The student has given an incorrect answer.

88
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
FOURTH OPEN-ENDED QUESTION
C-G.1.1.2
Question 49

89
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 49

90
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
ITEM-SPECIFIC SCORING GUIDELINE
Question #49
Grade 5
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
M05.C-G.1—Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
M05.C-G.1.1—Identify parts of a coordinate grid and describe or interpret points given an ordered pair.
M05.C-G.2.1—Use basic properties to classify two-dimensional figures.
Scoring Guide:
Score In this item, the student –
4
Demonstrates a thorough understanding of how to graph points on the coordinate
plane to solve real-world problems by correctly solving problems and clearly explaining
procedures.
3
Demonstrates a general understanding of how to graph points on the coordinate plane to
solve real-world problems by correctly solving problems and clearly explaining procedures
with only minor errors or omissions.
2
Demonstrates a partial understanding of how to graph points on the coordinate plane to
solve real-world problems by correctly performing a significant portion of the required task.
1
Demonstrates minimal understanding of how to graph points on the coordinate plane to
solve real-world problems.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Non-
Scorables
B – Blank
R – Refusal
K – Off task/topic
F – Foreign language
U – Illegible
Top Scoring Student Response And Training Notes:
Score Description
4 Student earns 4 points.
3 Student earns 3.0 – 3.5 points.
2 Student earns 2.0 – 2.5 points.
1
Student earns 0.5 – 1.5 points.
OR
Student demonstrates minimal understanding of how to graph points on the coordinate
plane to solve real-world problems.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or concept
being measured.

91
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question #49
Top Scoring Response:
Part A Answer
What? Why?
(2 score points)
½ point for each correct point
½ point for each correct label
Part B Answer
What? Why?
point R: (8, 0)
point T: (2, 6)
Sample Explanation:
Since point R is on the x-axis, its y-coordinate must be 0. It also has to be the same
distance from point Q and point S, so point R must be at (8, 0) since this point is 6
units away from both point Q and point S. Point T must also be 6 units away from
point Q and point S, so it must be at (2, 6) since that point is 6 units above point Q
and 6 units to the left of point S.
OR equivalent
(2 score points)
½ point for each ordered pair
1 point for correct and complete explanation
OR ½ point for correct but incomplete explanation
Note: Student must write the ordered pairs with parentheses and commas for credit; no credit for writing the
correct order pairs in the wrong space.

92
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
FOURTH OPEN-ENDED QUESTION RESPONSES
C-G.1.1.2 Response Score: 4
Question 49
The student has plotted two correct points.
The student has given two correct labels.

93
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 49
The student has given two correct answers.
The student has given a complete explanation.

94
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2 Response Score: 3
Question 49
The student has plotted two correct points.
The student has given two correct labels.

95
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 49
The student has given two correct answers.
The student has given a correct but incomplete explanation.

96
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2 Response Score: 2
Question 49
The student has plotted two correct points.
The student has given no correct labels.

97
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 49
The student has given no correct answers.
The student has given a complete explanation.

98
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2 Response Score: 1
Question 49
The student has plotted one correct point.
The student has given one correct label.

99
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 49
The student has given one correct answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

100
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
C-G.1.1.2 Response Score: 0
Question 49
The student has plotted no correct points.
The student has given no correct labels.

101
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question 49
The student has given no correct answers.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

102
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
50. Grace is sorting her buttons for a craft project. Her buttons are shown below. Each
button is labeled with its width.
1 inches
1 inch
1 inch
1 inch
1
4
inch
3
4
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
A. Create a line plot for the widths of the buttons.
Grace’s Buttons
0
21
Grace’s Buttons
Width (inches)
Go to the next page to finish question 50.
FIFTH OPEN-ENDED QUESTION
D-M.2

103
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Grace lines up only the widest buttons in a row. There are no spaces between
the buttons.
B. What is the length, in inches, of the row of buttons?
Grace finds another button. The button does not match the width of any of her
other buttons. It is not the biggest nor the smallest button in her collection. She
could add the width of the button to the line plot without adding any new tick
marks on the number line.
C. Explain how to determine all the possible widths of Grace’s new button.
As part of your explanation, include all the possible widths.
50. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.

104
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
ITEM-SPECIFIC SCORING GUIDELINE
Question #50
Grade 5
Assessment Anchor this item will be reported under:
M05.D-M.2—Represent and interpret data.
Specific Anchor Descriptor addressed by this item:
M05.D-M.2.1—Organize, display, and answer questions based on data.
Scoring Guide:
Score
In this item, the student –
4
Demonstrates a thorough understanding of how to represent and interpret data by
correctly solving problems and clearly explaining procedures.
3
Demonstrates a general understanding of how to represent and interpret data by correctly
solving problems and clearly explaining procedures with only minor errors or omissions.
2
Demonstrates a partial understanding of how to represent and interpret data by correctly
performing a significant portion of the required task.
1 Demonstrates minimal understanding of how to represent and interpret data.
0
The response has no correct answer and insufficient evidence to demonstrate any
understanding of the mathematical concepts and procedures as required by the task.
Response may show only information copied from the question.
Non-
Scorables
B – Blank
R – Refusal
K – Off task/topic
F – Foreign language
U – Illegible
Top Scoring Student Response And Training Notes:
Score
Description
4 Student earns 4 points.
3 Student earns 3.0 – 3.5 points.
2 Student earns 2.0 – 2.5 points.
1
Student earns 0.5 – 1.5 points.
OR
Student demonstrates minimal understanding of how to represent and interpret data.
0
Response is incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or concept
being measured.

105
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Question #50
Top Scoring Response:
Part A Answer
What? Why?
Grace’s Buttons
Width (inches)
0
21
(1 score point)
1 point for correct answer
OR ½ point for 10 correct Xs
[Note: Students cannot receive a “4” if they incorrectly add additional number labels]
Part B Answer
What? Why?
6
1
}
4
(inches)
[Note: Carry over any error from Part A]
(1 score point)
1 point for correct answer
Part C Answer
What? Why?
Since the button is not the biggest or smallest in Grace’s collection, it must be
between
1
}
2
and 1
1
}
4
. Also, since it does not match the width of any of her other
buttons, there are three possible widths for Grace’s new button:
5
}
8
inch,
7
}
8
inch,
or 1
1
}
8
inches.
[Note: Carry over any error from Part A]
(2 score points)
1 point for all 3 correct widths
1 point for complete explanation
OR ½ point for correct but incomplete explanation

106
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
50. Grace is sorting her buttons for a craft project. Her buttons are shown below. Each
button is labeled with its width.
1 inches
1 inch
1 inch
1 inch
1
4
inch
3
4
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
A. Create a line plot for the widths of the buttons.
Grace’s Buttons
0
21
Grace’s Buttons
Width (inches)
Go to the next page to finish question 50.
D-M.2 Response Score: 4
FIFTH OPEN-ENDED QUESTION RESPONSES
The student has given a correct answer.

107
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Grace lines up only the widest buttons in a row. There are no spaces between
the buttons.
B. What is the length, in inches, of the row of buttons?
Grace finds another button. The button does not match the width of any of her
other buttons. It is not the biggest nor the smallest button in her collection. She
could add the width of the button to the line plot without adding any new tick
marks on the number line.
C. Explain how to determine all the possible widths of Grace’s new button.
As part of your explanation, include all the possible widths.
50. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given 3 correct widths.
The student has given a complete explanation.

108
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
50. Grace is sorting her buttons for a craft project. Her buttons are shown below. Each
button is labeled with its width.
1 inches
1 inch
1 inch
1 inch
1
4
inch
3
4
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
A. Create a line plot for the widths of the buttons.
Grace’s Buttons
0
21
Grace’s Buttons
Width (inches)
Go to the next page to finish question 50.
D-M.2 Response Score: 3
The student has given 10 correct Xs.

109
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Grace lines up only the widest buttons in a row. There are no spaces between
the buttons.
B. What is the length, in inches, of the row of buttons?
Grace finds another button. The button does not match the width of any of her
other buttons. It is not the biggest nor the smallest button in her collection. She
could add the width of the button to the line plot without adding any new tick
marks on the number line.
C. Explain how to determine all the possible widths of Grace’s new button.
As part of your explanation, include all the possible widths.
50. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given a correct answer, based on part A.
The student has given 3 correct widths.
The student has given a correct but incomplete explanation.
110
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
50. Grace is sorting her buttons for a craft project. Her buttons are shown below. Each
button is labeled with its width.
1 inches
1 inch
1 inch
1 inch
1
4
inch
3
4
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
A. Create a line plot for the widths of the buttons.
Grace’s Buttons
0
21
Grace’s Buttons
Width (inches)
Go to the next page to finish question 50.
D-M.2 Response Score: 2
The student has given a correct answer.

111
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Grace lines up only the widest buttons in a row. There are no spaces between
the buttons.
B. What is the length, in inches, of the row of buttons?
Grace finds another button. The button does not match the width of any of her
other buttons. It is not the biggest nor the smallest button in her collection. She
could add the width of the button to the line plot without adding any new tick
marks on the number line.
C. Explain how to determine all the possible widths of Grace’s new button.
As part of your explanation, include all the possible widths.
50. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given a correct answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

112
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
50. Grace is sorting her buttons for a craft project. Her buttons are shown below. Each
button is labeled with its width.
1 inches
1 inch
1 inch
1 inch
1
4
inch
3
4
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
A. Create a line plot for the widths of the buttons.
Grace’s Buttons
0
21
Grace’s Buttons
Width (inches)
Go to the next page to finish question 50.
D-M.2 Response Score: 1
The student has given an incorrect answer.

113
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Grace lines up only the widest buttons in a row. There are no spaces between
the buttons.
B. What is the length, in inches, of the row of buttons?
Grace finds another button. The button does not match the width of any of her
other buttons. It is not the biggest nor the smallest button in her collection. She
could add the width of the button to the line plot without adding any new tick
marks on the number line.
C. Explain how to determine all the possible widths of Grace’s new button.
As part of your explanation, include all the possible widths.
50. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given a correct but incomplete explanation.

114
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
50. Grace is sorting her buttons for a craft project. Her buttons are shown below. Each
button is labeled with its width.
1 inches
1 inch
1 inch
1 inch
1
4
inch
3
4
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
1 inches
1
4
1 inches
1
4
inch
1
2
A. Create a line plot for the widths of the buttons.
Grace’s Buttons
0
21
Grace’s Buttons
Width (inches)
Go to the next page to finish question 50.
D-M.2 Response Score: 0
The student has given an incorrect answer.

115
PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics Item and Scoring Sampler—September 2015
PSSA MATHEMATICS
Grace lines up only the widest buttons in a row. There are no spaces between
the buttons.
B. What is the length, in inches, of the row of buttons?
Grace finds another button. The button does not match the width of any of her
other buttons. It is not the biggest nor the smallest button in her collection. She
could add the width of the button to the line plot without adding any new tick
marks on the number line.
C. Explain how to determine all the possible widths of Grace’s new button.
As part of your explanation, include all the possible widths.
50. Continued. Please refer to the previous page for task explanation.
The student has given an incorrect answer.
The student has given an incorrect explanation.

PSSA Grade 5 Mathematics
Item and Scoring Sampler
Copyright © 2015 by the Pennsylvania Department of Education. The materials contained in this publication may be
duplicated by Pennsylvania educators for local classroom use. This permission does not extend to the duplication
of materials for commercial use.
