
GX Works2 Beginner's Manual
(Simple Project)
-SW1DND-GXW2-E
-SW1DNC-GXW2-E

A - 1
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
(Always read these instructions before using this product.)
Before using this product, thoroughly read this manual and the relevant manuals introduced in this manual
and pay careful attention to safety and handle the products properly. If products are used in a different way
from that specified by manufacturers, the protection function of the products may not work properly.
The precautions given in this manual are concerned with this product. For the safety precautions of the
programmable controller system, refer to the User’s Manual for the CPU module.
In this manual, the safety precautions are ranked as " WARNING" and " CAUTION".
Note that the CAUTION level may lead to serious consequences according to the circumstances.
Always follow the precautions of both levels because they are important for personal safety.
Please save this manual to make it accessible when required and always forward it to the end user.
[Design Instructions]
[Security Precautions]
WARNING
When data change, program change, or status control is performed from a personal computer to a running
programmable controller, create an interlock circuit outside the programmable controller to ensure that the whole
system always operates safely.
Furthermore, for the online operations performed from a personal computer to a programmable controller CPU, the
corrective actions against a communication error due to such as a cable connection fault should be predetermined as
a system.
WARNING
To maintain the security (confidentiality, integrity, and availability) of the programmable controller and the system
against unauthorized access, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, computer viruses, and other cyberattacks from external
devices via the network, take appropriate measures such as firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and antivirus
solutions.
WARNING
CAUTION
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in
death or severe injury.
Indicates that incorrect handling may cause hazardous conditions, resulting in
minor or moderate injury or property damage.

A - 2
[Startup and Maintenance Instructions]
CAUTION
The online operations performed from a personal computer to a running programmable controller CPU (Program
change when a programmable controller CPU is RUN, operating status changes such as forced input/output
operation and RUN-STOP switching, and remote control operation) must be executed after the manual has been
carefully read and the safety has been ensured.
When changing a program while a programmable controller CPU is RUN, it may cause a program corruption in some
operating conditions. Fully understand the precautions described in GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual
(Common) before use.
The positioning test functions of OPR, JOG, inching or positioning data for QD75/LD75 positioning module must be
executed with the programmable controller set to STOP after the manual has been carefully read and the safety has
been ensured. Specially when executing the function on the network system, ensure the safety thoroughly since the
machinery whose operation cannot be checked by an operator may be activated. The operation failure may cause the
injury or machine damage.

A - 3
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
(1) MELSEC programmable controller ("the PRODUCT") shall be used in conditions;
i) where any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT, if any, shall not lead to any major or serious accident;
and
ii) where the backup and fail-safe function are systematically or automatically provided outside of the PRODUCT for the
case of any problem, fault or failure occurring in the PRODUCT.
(2) The PRODUCT has been designed and manufactured for the purpose of being used in general industries.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC SHALL HAVE NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO
ANY AND ALL RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY BASED ON CONTRACT, WARRANTY, TORT, PRODUCT
LIABILITY) FOR ANY INJURY OR DEATH TO PERSONS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO PROPERTY CAUSED BY the
PRODUCT THAT ARE OPERATED OR USED IN APPLICATION NOT INTENDED OR EXCLUDED BY
INSTRUCTIONS, PRECAUTIONS, OR WARNING CONTAINED IN MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC USER'S, INSTRUCTION
AND/OR SAFETY MANUALS, TECHNICAL BULLETINS AND GUIDELINES FOR the PRODUCT.
("Prohibited Application")
Prohibited Applications include, but not limited to, the use of the PRODUCT in;
• Nuclear Power Plants and any other power plants operated by Power companies, and/or any other cases in which the
public could be affected if any problem or fault occurs in the PRODUCT.
• Railway companies or Public service purposes, and/or any other cases in which establishment of a special quality
assurance system is required by the Purchaser or End User.
• Aircraft or Aerospace, Medical applications, Train equipment, transport equipment such as Elevator and Escalator,
Incineration and Fuel devices, Vehicles, Manned transportation, Equipment for Recreation and Amusement, and
Safety devices, handling of Nuclear or Hazardous Materials or Chemicals, Mining and Drilling, and/or other
applications where there is a significant risk of injury to the public or property.
Notwithstanding the above restrictions, Mitsubishi Electric may in its sole discretion, authorize use of the PRODUCT in
one or more of the Prohibited Applications, provided that the usage of the PRODUCT is limited only for the specific
applications agreed to by Mitsubishi Electric and provided further that no special quality assurance or fail-safe,
redundant or other safety features which exceed the general specifications of the PRODUCTs are required. For details,
please contact the Mitsubishi Electric representative in your region.
(3) Mitsubishi Electric shall have no responsibility or liability for any problems involving programmable controller trouble and
system trouble caused by DoS attacks, unauthorized access, computer viruses, and other cyberattacks.

A - 4
REVISIONS
The manual number is written at the bottom left of the back cover.
Print date Manual number Revision
Jul., 2008 SH(NA)-080787ENG-A First edition
Jan., 2009 SH(NA)-080787ENG-B
Q00UJ, Q00U, Q01U, Q10UDH, Q10UDEH, Q20UDH, Q20UDEH, FXCPU
MANUALS, Section 1.1, Section 3.6, Section 4.1
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL, Section 1,
Section 2.2, Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.5, Section 3.2.6, Section 3.2.7,
Section 3.2.8, Section 3.3.1, Section 3.3.2, Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.2,
Section 4.1.2, Section 4.2.6, Section 4.4.1
Jul., 2009 SH(NA)-080787ENG-C
Q00J, Q00, Q01
MANUALS, Section 1.1, Section 2.2, Section 4.2
MANUALS, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.3, Section 3.4, Section 3.5,
Section 3.6, Section 3.7, Section 3.8, Section 3.9, Section 4.1, Section 4.2,
Section 4.4, Section 4.7
Oct., 2009 SH(NA)-080787ENG-D
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, Section 1.2, Section 3.2.3, Section 3.2.5, Section 3.7.1,
Section 3.7.2, Section 3.7.3, Section 3.8, Section 3.9, Section 4.2.5
Jan., 2010 SH(NA)-080787ENG-E
L02, L26-BT
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.3, Section 3.2.4, Section 3.2.5,
Section 3.2.6, Section 3.2.8, Section 3.3.2, Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.2,
Section 3.5, Section 3.6, Section 3.7.2, Section 3.7.4, Section 4.2.6, Section 4.4.1
Apr., 2010 SH(NA)-080787ENG-F
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS
IN THIS MANUAL, Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.3, Section 3.2.8,
Section 3.3.1, Section 3.3.2, Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.2, Section 3.5, Section 3.9,
Section 4.2.6, Section 4.4.1
Model Addition
Addition
Correction
Model Addition
Addition
Correction
Correction
Model Addition
Addition
Correction
Correction

A - 5
Print date Manual number Revision
Sep., 2010 SH(NA)-080787ENG-G
Section 4.2.7
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL, Section 3.2.2,
Section 3.2.3, Section 3.2.6, Section 3.3.1, Section 3.3.2, Section 3.5, Section 3.6,
Section 4.1.2, Section 4.2.3, Section 4.2.5, Section 4.2.6, Section 4.2.8
Jan., 2011 SH(NA)-080787ENG-H
MANUALS, Section 2.1, Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.3,
Section 3.2.4, Section 3.2.5, Section 3.2.6, Section 3.2.8, Section 3.3.1,
Section 3.3.2, Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.2, Section 3.5, Section 3.6, Section 3.7.2,
Section 3.7.3, Section 3.7.4, Section 3.8, Section 4.2.6, Section 4.2.7, Section 4.4.1,
Section 4.7
Jul., 2011 SH(NA)-080787ENG-I
MANUALS, Section 1.1, Section 2.2, Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.3,
Section 3.2.6, Section 3.2.7, Section 3.2.8, Section 3.3.2, Section 3.4.1,
Section 3.4.2, Section 3.6, Section 3.7.1, Section 3.7.2, Section 3.7.3, Section 3.8,
Section 3.9, Section 4.1.2, Section 4.2.6, Section 4.2.7, Section 4.4.1
Jan., 2012 SH(NA)-080787ENG-J
MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 3.2.3, Section 3.2.6, Section 3.3.1, Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.2,
Section 3.8, Section 4.2.6, Section 4.2.7, Section 4.2.8, Section 4.4.1
May, 2012 SH(NA)-080787ENG-K
MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.3, Section 3.2.5, Section 3.2.6,
Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.2, Section 4.2.6, Section 4.2.7, Section 4.4.1
Feb., 2013 SH(NA)-080787ENG-L
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 3.2.6, Section 3.2.8, Section 3.3.2, Section 3.4.1, Section 3.4.2, Section 3.5,
Section 4.2.6, Section 4.2.7, Section 4.4.1
May, 2013 SH(NA)-080787ENG-M
Q04UDPV, Q06UDPV, Q13UDPV, Q26UDPV, L02S-P, L06-P, L26-P, FX
3S
MANUALS, GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL,
Section 3.2.1, Section 3.2.2, Section 3.2.3, Section 3.3.1
Dec., 2013 SH(NA)-080787ENG-N
Section 3.2.3, Section 3.8, Section 3.9
Jun., 2014 SH(NA)-080787ENG-O Front cover correction
Addition
Correction
Correction
Correction
Correction
Correction
Correction
Model Addition
Correction
Correction

A - 6
Japanese Manual Version SH-080733-V
2008 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORPORATION
Print date Manual number Revision
Jun., 2015 SH(NA)-080787ENG-P
Section 3.4.2
Jan., 2018 SH(NA)-080787ENG-Q
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL
Jun., 2018 SH(NA)-080787ENG-R
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Sep., 2022 SH(NA)-080787ENG-S
COPYRIGHTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS, CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT
Jun., 2023 SH(NA)-080787ENG-T
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
This manual confers no industrial property rights or any rights of any other kind, nor does it confer any patent licenses.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation cannot be held responsible for any problems involving industrial property rights which may occur
as a result of using the contents noted in this manual.
Correction
Correction
Correction
Addition
Correction
Correction

A - 7
INTRODUCTION
Thank you for purchasing the engineering software, MELSOFT series.
Before using the product, thoroughly read this manual to develop full familiarity with the functions and performance
to ensure correct use.
CONTENTS
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ...................................................................................................................... A - 1
CONDITIONS OF USE FOR THE PRODUCT ...................................................................................... A - 3
REVISIONS ........................................................................................................................................... A - 4
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................... A - 7
CONTENTS ........................................................................................................................................... A - 7
MANUALS.............................................................................................................................................. A - 9
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL........................................................... A - 17
1OVERVIEW
1.1 Simple Project and Structured Project 1 - 2
1.2 Program Creation Procedure 1 - 4
2 CREATED PROGRAM AND SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1 System Configuration 2 - 2
2.2 Overview of Program Creation 2 - 2
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.1 Created Program 3 - 2
3.1.1 Operations of program.................................................................................................................. 3 - 2
3.1.2 Created program .......................................................................................................................... 3 - 2
3.2 Creating a Project 3 - 3
3.2.1 Starting GX Works2......................................................................................................................3 - 3
3.2.2 Screen configuration in GX Works2 .............................................................................................3 - 4
3.2.3 Creating a new project.................................................................................................................. 3 - 5
3.2.4 Setting parameters .......................................................................................................................3 - 7
3.2.5 Setting labels ................................................................................................................................3 - 8
3.2.6 Creating a program..................................................................................................................... 3 - 11
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks............................................................................................................3 - 16
3.2.8 Compiling a program .................................................................................................................. 3 - 17
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller 3 - 19
3.3.1 Connecting the personal computer to the programmable controller...........................................3 - 19
3.3.2 Writing a project to the programmable controller........................................................................ 3 - 24
3.4 Monitoring Operations 3 - 27
3.4.1 Monitoring a program ................................................................................................................. 3 - 27
3.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values.............................................................................................. 3 - 32

A - 8
3.5 Diagnosing the programmable controller 3 - 36
3.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller 3 - 37
3.7 Printing 3 - 39
3.7.1 Setting the printer....................................................................................................................... 3 - 39
3.7.2 Previewing a program ................................................................................................................ 3 - 40
3.7.3 Printing a program...................................................................................................................... 3 - 42
3.7.4 Previewing a PLC Parameter..................................................................................................... 3 - 43
3.7.5 Printing a PLC Parameter .......................................................................................................... 3 - 44
3.8 Saving a Project 3 - 45
3.9 Exiting GX Works2 3 - 46
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
4.1 Created Program 4 - 2
4.1.1 Operations of program ................................................................................................................. 4 - 2
4.1.2 Created Program.......................................................................................................................... 4 - 3
4.2 Created Program 4 - 4
4.2.1 Starting GX Works2 ..................................................................................................................... 4 - 4
4.2.2 Screen configuration in GX Works2............................................................................................. 4 - 4
4.2.3 Creating a new project ................................................................................................................. 4 - 4
4.2.4 Setting parameters....................................................................................................................... 4 - 4
4.2.5 Setting labels (for QCPU/LCPU) .................................................................................................. 4 - 5
4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)......................................................................................... 4 - 6
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU) ............................................................................................... 4 - 15
4.2.8 Compiling a program (for QCPU/LCPU) or converting an SFC diagram (for FXCPU) .............. 4 - 26
4.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller 4 - 27
4.4 Monitoring Operations 4 - 27
4.4.1 Monitoring a program ................................................................................................................. 4 - 27
4.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values ............................................................................................. 4 - 29
4.5 Diagnosing the programmable controller 4 - 30
4.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller 4 - 30
4.7 Printing 4 - 30
4.8 Saving a Project 4 - 30
4.9 Exiting GX Works2 4 - 30
TRADEMARKS
COPYRIGHTS
A - 9
MANUALS
Related manuals are separately issued according to the purpose of their functions for GX Works2.
Related manuals
The manuals related to this product are shown below.
Refer to the following tables when ordering required manuals.
1) Operation of GX Works2
2) Structured Programming
Manual name
Manual number
(Manual code)
GX Works2 Beginner’s Manual (Simple Project)
Explains fundamental operation methods such as creating, editing, and monitoring programs in Simple
project for users inexperienced with GX Works2. (Sold separately)
SH-080787ENG
(13JZ22)
(this manual)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
Explains the system configuration of GX Works2 and the functions common to a Simple project and
Structured project such as parameter setting and the operating method for the online function.
(Sold separately)
SH-080779ENG
(13JU63)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Explains operation methods such as creating and monitoring programs in Simple project of GX Works2.
(Sold separately)
SH-080780ENG
(13JU64)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project, Function Block)
Explains methods for such as creating function blocks, pasting function blocks to sequence programs,
and operating FB library in Simple project of GX Works2. (Sold separately)
SH-080984ENG
(13JU72)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Structured Project)
Explains operation methods such as creating and monitoring programs in Structured project of GX Works2.
(Sold separately)
SH-080781ENG
(13JU65)
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Intelligent Function Module)
Explains operation methods of intelligent function module such as parameter setting, monitoring programs,
and predefined protocol support function in GX Works2. (Sold separately)
SH-080921ENG
(13JU69)
GX Works2 Beginner’s Manual (Structured Project)
Explains fundamental operation methods such as creating, editing and monitoring programs in Structured
project for users inexperienced with GX Works2. (Sold separately)
SH-080788ENG
(13JZ23)
Manual name
Manual number
(Manual code)
MELSEC-Q/L/F Structured Programming Manual (Fundamentals)
Explains the programming methods, types of programming languages, and other information required to
create structured programs. (Sold separately)
SH-080782ENG
(13JW06)
MELSEC-Q/L Structured Programming Manual (Common Instructions)
Explains the specifications and functions of common instructions such as sequence instructions, basic
instructions, and application instructions, that can be used in structured programs. (Sold separately)
SH-080783ENG
(13JW07)
MELSEC-Q/L Structured Programming Manual (Application Functions)
Explains the specifications and functions of application functions that can be used in structured programs.
(Sold separately)
SH-080784ENG
(13JW08)
MELSEC-Q/L Structured Programming Manual (Special Instructions)
Explains the specifications and functions of special instructions such as module dedicated instruction, PID
control instruction, and built-in I/O function dedicated instruction, that can be used in structured programs.
(Sold separately)
SH-080785ENG
(13JW09)
FXCPU Structured Programming Manual [Device & Common]
Explains the devices and parameters provided in GX Works2 for structured programming. (Sold separately)
JY997D26001
(09R925)
FXCPU Structured Programming Manual [Basic & Applied Instruction]
Explains the sequence instructions provided in GX Works2 for structured programming. (Sold separately)
JY997D34701
(09R926)

A - 10
3) Operation of iQ Works
FXCPU Structured Programming Manual [Application Functions]
Explains the application functions provided in GX Works2 for structured programming. (Sold separately)
JY997D34801
(09R927)
Manual name
Manual number
(Manual code)
Let's start iQ Works Version 2
Explains fundamental operation methods such as managing the system using MELSOFT Navigator and
using system labels for users inexperienced with GX Works2. (Sold separately)
SH-081261ENG
(13JZ79)
The Operating Manuals are included on the DVD and CD of the software package in a PDF file format.
Manuals in printed form are sold separately for single purchase. Order a manual by quoting the manual
number (model code) listed in the table above.
Manual name
Manual number
(Manual code)

A - 11
Purpose of this manual
This manual explains the operation for creating sequence programs in Simple project, one of the
functions supported with GX Works2.
Manuals for reference are listed in the following table according to their purpose.
For information such as the contents and manual number of each manual, refer to the list of 'Related
manuals'.
1) Installation of GX Works2 and USB driver
2) Operation of GX Works2
Purpose
GX Works2
Installation
Instructions
GX Works2 Version 1
Operating Manual
Common
Learning the operating environment and
installation method
Learning a USB driver
installation method
Purpose
GX Works2
Beginner’s Manual
GX Works2 Version 1
Operating Manual
Simple
Project
Structured
Project
Common
Simple Project
Structured
Project
Intelligent
Function
Module
Function
Block
Learning all functions of GX Works2
Learning the project types and available
languages in GX Works2
Learning the basic operations and
operating procedures when creating a
simple project for the first time
Learning the basic operations and
operating procedures when creating a
structured project for the first time
Learning the operations of available
functions regardless of project type.
Learning the functions and operation
methods for programming
Learning the operations and operating
procedures when creating function
blocks (FB) in Simple project.
Learning data setting methods for
intelligent function module
Details
Details
Outline
Outline
Details
Details
Details
Outline
Details Details
Details
Details

A - 12
3) Operations in each programming language
For details of instructions used in each programming language, refer to the section 4 / section 5 on
the next page.
*1: MELSAP3 and FX series SFC only
Purpose
GX Works2
Installation
Instructions
GX Works2
Beginner’s Manual
GX Works2 Version 1
Operating Manual
Simple
Project
Structured
Project
Common
Simple
Project
Structured
Project
Intelligent
Function
Module
Simple
Project
Ladder
SFC
ST
Structured
Project
Ladder
SFC
Structured Ladder/FBD
ST
Outline
Details
Outline
*1
Details
Outline
Details
Outline
Details
Outline
*1
Details
Outline
Details
Outline
Details

A - 13
4) Details of instructions in each programming language (for QCPU (Q mode)/LCPU)
Purpose
MELSEC-
Q/L/F
Structured
Programming
Manual
MELSEC-Q/L Structured
Programming Manual
MELSEC-
Q/L
Programming
Manual
MELSEC-Q/L/QnA
Programming Manual
Manual for
module to
be used
Fundamentals
Common
Instructions
Special
Instructions
Application
Functions
Common
Instructions
PID Control
Instructions
SFC -
All
languages
Learning details of
programmable
controller CPU
error codes,
special relays, and
special registers
Using
ladder
language
Learning the types
and details of
common
instructions
Learning the types
and details of
instructions for
intelligent function
modules
Learning the types
and details of
instructions for
network modules
Learning the types
and details of
instructions for the
PID control
function
Using
SFC
language
Learning details of
specifications,
functions, and
instructions of
SFC (MELSAP3)
Using
Structured
Ladder/
FBD or ST
language
Learning the
fundamentals for
creating a
structured
program
Learning the types
and details of
common
instructions
Learning the types
and details of
instructions for
intelligent function
modules
Learning the types
and details of
instructions for
network modules
Learning the types
and details of
instructions for the
PID control
function
Learning the types
and details of
application
functions
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Outline
Details
Outline
Details
Outline
Details
Details

A - 14
5) Details of instructions in each programming language (for FXCPU)
Purpose
MELSEC-
Q/L/F
Structured
Programming
Manual
FXCPU Structured Programming Manual
FXCPU Programming Manual
Fundamentals
Device &
Common
Basic &
Applied
Instruction
Application
Functions
FX0, FX0S,
FX
0N, FX1,
FX
U, FX2C
FX1S, FX1N,
FX
2N, FX1NC,
FX
2NC
FX3S,
FX
3G, FX3U,
FX
3GC, FX3UC
Using ladder
language
Learning the types
and details of
basic/application
instructions,
descriptions of
devices and
parameters
Using SFC
language
Learning details of
specifications,
functions, and
instructions of SFC
Using
Structured
Ladder/FBD
or ST
language
Learning the
fundamentals for
creating a
structured program
Learning the
descriptions of
devices,
parameters, and
error codes
Learning the types
and details of
sequence
instructions
Learning the types
and details of
application
instructions
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details
Details

A - 15
How to read this manual
Section title
Clarifies the section of currently
opened page.
Chapter heading
Index on the right of the page
number clarifies the chapter of
currently opened page.
Reference location
leads to the reference
location and reference manuals.
* Since the above page was created for explanation purpose, it differs from the actual page.
Section title
Clarifies the section of currently
opened page.

A - 16
This manual also uses the following columns:
This explains notes for requiring attention or useful functions relating to the information given on the
same page.
This explains restrictions relating to the information given on the same page.
Symbols used in this manual
The following shows the symbols used in this manual with descriptions and examples.
Restrictions
No. Symbol Description Example
(1) [ ] Menu name on a menu bar [Project]
(2) Toolbar icon
(3) << >> Tab name in a screen <<PLC System>>
(4) Button on a screen
button
(5) " " Item name in a screen "Timer Limit Setting"
Keyboard key

A - 17
GENERIC TERMS AND ABBREVIATIONS IN THIS MANUAL
This manual uses the generic terms and abbreviations listed in the following table to discuss the
software packages and programmable controller CPUs. Corresponding module model names are also
listed if needed.
Generic terms and
Abbreviations
Description
GX Works2
Generic product name for SWnDND-GXW2-E and SWnDNC-GXW2-E
(n: version)
Existing application -
GX Developer
Generic product name for SWnD5C-GPPW-E, SWnD5C-GPPW-EA, SWnD5C-GPPW-EV, and
SWnD5C-GPPW-EVA
(n: version)
GX Simulator
Generic product name for SWnD5C-GPPW-E, SWnD5C-GPPW-EA, SWnD5C-GPPW-EV, and
SWnD5C-GPPW-EVA
(n: version)
iQ Works Abbreviation for MELSOFT iQ Works
Personal computer
Generic term for personal computers on which Windows
®
operates
Q series Abbreviation for Mitsubishi Electric programmable controller MELSEC-Q series
L series Abbreviation for Mitsubishi Electric programmable controller MELSEC-L series
FX series Abbreviation for Mitsubishi Electric programmable controller MELSEC-F series
Basic model QCPU Generic term for Q00J, Q00, Q01
High Performance model
QCPU
Generic term for Q02, Q02H, Q06H, Q12H, and Q25H
Universal model QCPU
Generic term for Q00UJ, Q00U, Q01U, Q02U, Q03UD, Q03UDE, Q03UDV, Q04UDH,
Q04UDEH, Q04UDV, Q04UDPV, Q06UDH, Q06UDEH, Q06UDV, Q06UDPV, Q10UDH,
Q10UDEH, Q13UDH, Q13UDEH, Q13UDV, Q13UDPV, Q20UDH, Q20UDEH, Q26UDH,
Q26UDEH, Q26UDV, Q26UDPV, Q50UDEH, and Q100UDEH
QCPU (Q mode)
Generic term for Basic model QCPU, High Performance model QCPU, Process CPU,
Redundant CPU, and Universal model QCPU
LCPU Generic term for L02S, L02S-P, L02, L02-P, L06, L06-P, L26, L26-P, L26-BT, and L26-PBT
FXCPU
Generic term for FX
0S, FX0, FX0N, FX1S, FX1N, FX1NC, FXU, FX2C, FX2N, FX2NC, FX3S, FX3G,
FX
3GC, FX3U, and FX3UC
CPU module Generic term for QCPU (Q mode), LCPU, and FXCPU
SFC Generic term for MELSAP3, MELSAP-L, and FX series SFC

A - 18
MEMO

1 - 1
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
1OVERVIEW
This manual explains the procedures to actually create a program (Simple Project) using GX Works2 and
operate the programmable controller using the created program.
If this is your first time creating a Simple Project using GX Works2, you are recommended to read this manual
first, and then use GX Works2.
Refer to the following manual for Structured Projects:
GX Works2 Beginner’s Manual (Structured Project)
1.1 Simple Project and Structured Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.2 Program Creation Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4

1 - 2
1 OVERVIEW
1.1 Simple Project and Structured Project
Simple Project
In a Simple Project, you can create sequence programs using instructions for programmable controller
CPU.
The Simple Project offers the same operability for program creation as the conventional GX Developer.
You can create sequence programs using the following programming languages:
Graphic languages
• Ladder
Use this graphic language to describe programs as ladders consisting of contacts, coils, etc.,
using the same operating procedures as the conventional GX Developer.
•SFC
Use this graphic language to describe sequence control in a way easy to understand.
Describe steps which specify the processing and transition conditions which specify conditions
for proceeding to the next step.
You can describe steps and transition conditions using the ladder language.
Text language
• ST (Structured Text)
This text language allows you to describe controls by syntax including alternative sequences
offered by conditional sentences and repetition offered by repetition sentences in the same way
as high-level languages such as the C language. Accordingly, you can briefly create programs
easy to look at.
Structured Project
In a Structured Project, you can create programs by structured program.
By dividing controls into small portions and making parts of common contents, you can create programs
easy to understand and applicable to many cases (by structured program.)
You can create sequence programs using the following programming languages:
Graphic languages
• Ladder
Use this graphic language to describe programs as ladders consisting of contacts, coils, etc.,
using the same operating procedures as the conventional GX Developer.
• Structured Ladder/FBD
Structured Ladder is created based on the relay circuit design technology. Because this
language is easy to understand intuitively, it is used generally for sequence programs.
Every ladder always starts from a base line on the left.
Structured Ladder consists of contacts, coils, function blocks and functions which are connected
each other with vertical lines and horizontal lines.
FBD connects functions and function blocks with ruled lines to describe ladders.
•SFC
Use this graphic language to describe sequence control in a way easy to understand.
Describe steps which specify the processing and transition conditions which specify conditions
for proceeding to the next step.
You can describe steps and transition conditions using the ladder language.

1 - 3
1.1 Simple Project and Structured Project
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
Text language
• ST (Structured Text)
This text language allows you to describe controls by syntax including alternative sequences
offered by conditional sentences and repetition offered by repetition sentences in the same way
as high-level languages such as the C language. Accordingly, you can briefly create programs
easy to look at.
Restrictions
The FXCPU does not support the ST language in Simple Project, and does not support the ladder language
and SFC language in Structured Project.

1 - 4
1 OVERVIEW
1.2 Program Creation Procedure
The figure below shows how to create a program with a Simple Project and execute it in a programmable
controller CPU.
1. Opening a project
2. Setting parameters
3. Setting labels
4. Editing the program
5. Conversion and compiling
Procedure Reference
Start GX Works2. 3.2.1
Create a new Simple Project. Or open an existing Simple Project. 3.2.3
Procedure Reference
Set the parameters. 3.2.4
Procedure Reference
Define global labels. 3.2.5
Define local labels. --
Procedure Reference
Edit the program in each program part.
3.2.6
4.2.6
4.2.7
Procedure Reference
Convert ladder blocks. 3.2.7
Compile the program. 3.2.8
(To the next page)

1 - 5
1.2 Program Creation Procedure
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
6. Connecting the programmable controller CPU
7. Writing to the programmable controller
8. Checking operations
9. Printing
10.Exiting GX Works2
Procedure Reference
Connect the personal computer to the programmable controller CPU.
3.3.1
Set the connection destination.
Procedure Reference
Write the parameters to the programmable controller CPU.
3.3.2
Write the program to the programmable controller CPU.
Procedure Reference
Monitor the sequence program execution status and device contents, and check
operations.
3.4
4.4
Check for errors in the programmable controller. 3.5
Procedure Reference
Print the program and parameters.
3.7
4.7
Procedure Reference
Save the project. 3.8
Exiting GX Works2. 3.9

1 - 6
1 OVERVIEW
MEMO

2 - 1
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
2 CREATED PROGRAM AND
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
This chapter explains the system configuration and gives an overview of the program created by using this
manual.
2.1 System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
2.2 Overview of Program Creation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2

2 - 2
2 CREATED PROGRAM AND SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
2.1 System Configuration
This manual uses GX Works2 and the Q Series programmable controller for explanation.
2.2 Overview of Program Creation
This manual explains the following program creation procedures using the simple example program shown in
the table below.
• Creating a new project
• Setting parameters
• Setting labels
• Creating a program (inputting contacts and application instructions, converting ladder blocks and compiling
the program)
• Writing to the programmable controller
• Monitoring ladder, etc.
•Preview, Printing
Table 2.1 Overview of created program
Program
language
Operation overview Reference
Ladder
You can create the Inline ST Box that displays ST language programs in the
Ladder Editor, and edit and monitor ST language programs.
Refer to the following manual for the details.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Chapter 3
SFC Chapter 4
ST
Refer to the following manual for the details.
GX Works2 Beginner’s Manual (Structured Project)
programmable controller (QCPU)
USB cable
GX Works2

3 - 1
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF
LADDER
This chapter explains how to create a program of Ladder with a Simple Project through a simple program
example.
3.1 Created Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.2 Creating a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller . . . . . . . . . 3-19
3.4 Monitoring Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
3.5 Diagnosing the programmable controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-36
3.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller . . . . . . . . . 3-37
3.7 Printing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-39
3.8 Saving a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
3.9 Exiting GX Works2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-46

3 - 2
3.1.1 Operations of program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.1 Created Program
This section explains the operations of the program to be created and ladder programs.
3.1.1 Operations of program
When X0 turns ON, the programmable controller turns ON Y10, and then turns OFF Y10 1 second
later.
When X1 turns ON, the programmable controller transfers K10 to D0 (which is defined with the Label
"VAR1").
When X2 turns ON, the programmable controller transfers K20 to D0 (which is defined with the Label
"VAR1").
3.1.2 Created program

3.2.1 Starting GX Works2
3 - 3
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
3.2 Creating a Project
Create a project using ladder programs.
3.2.1 Starting GX Works2
• Start GX Works2 from "MELSOFT" in Windows Start.
You can double-click the icon ( ) on the desktop to start the software package.

3 - 4
3.2.2 Screen configuration in GX Works2
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.2.2 Screen configuration in GX Works2
The GX Works2 screen has the following configuration.
Select "View" or "Hide" in the [View] menu for each of the Toolbar, Status bar, Navigation Window,
Function Block Selection window and Output window.
Refer to the following manual for the details on the GX Works2 screen configuration:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
View selection area
View contents display area
Title bar
Menu bar
Toolbar
Displays the contents of
the currently selected view.
Allows selection of the
view to be displayed.
Function Block selection
window
Displays the list of
function blocks available
to program creation.
Work window
Used for programming,
parameter setting,
monitoring, etc.
Output window
Displays the compile
result, error information
and warning information.
Status bar
Navigation Window

3.2.3 Creating a new project
3 - 5
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
3.2.3 Creating a new project
At first, create a project.
1. Perform either procedure below to display the
New Project screen.
• Select [Project] [New].
• Click (New).
2. Select the "Series", "Module Type", "Project
Type" and "Language" from the list boxes for
the new project to be created.
Check "Use Label" when using labels in the program
to be created.
After the setting, click the button.
Settings
• Series : QCPU (Q mode)
• Module Type : Q02/Q02H
• Project Type : Simple Project
• Language : Ladder
When using labels in Simple project, check "Use Label" on the New Project screen.
3. GX Works2 creates a new project.

3 - 6
3.2.3 Creating a new project
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
Opening an existing project
The Opening an existing project function has the single file format and workspace format screens.
Refer to the following manual for the details on the existing project opening procedure:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
1. Perform either operation below.
• Select [Project] [Open].
• Click (Open).
2. The Open Project screen appears.
3. Click the button to open the selected project.
Specify the existing project to be opened.
The selected project is displayed in
"File name".
Enter the folder where the
project is saved.

3.2.4 Setting parameters
3 - 7
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
3.2.4 Setting parameters
Set parameters.
1. Double-click "Parameter" "PLC Parameter"
on the Project view to display the Q Parameter
Setting screen.
2. Click the button to determine the
settings and close the screen.
The parameters remain unchanged from the initial
setting in the example in this manual.
Refer to the following manuals for the details on
parameter setting:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual
(Common)
Manual of the programmable controller
being used
Manual of the Network being used
Double-click it.
Click the [End]
button after
finishing the setting.

3 - 8
3.2.5 Setting labels
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.2.5 Setting labels
Set global labels.
When not using labels, proceed to Section 3.2.6.
1. Double-click "Global Label" "Global1" on the
Project view to display the Global Label Setting
screen.
2. Select the "Class" from the list box on the
Global Label Setting screen.
Settings
• Class: VAR_GLOBAL
3. Directly input the "Label Name" on the Global
Label Setting screen.
Settings
• Label Name: VAR1
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

3.2.5 Setting labels
3 - 9
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
Restrictions
Characters available for the label name
You can enter up to 32 characters as the label name.
However, note that the following label name will cause a compile error.
• Label name which contains space
• Label name whose first character is a number
• Label name equivalent to a device name
For other characters unavailable for the label name, refer to the following manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
4. Directly input the "Date Type" on the Global
Label Setting screen.
Settings
• Date Type: Word [Signed]
You can click to display the Type Selection screen, and then select the Types on this screen.
Settings
*1
1) Libraries : ALL
2) Type Class : Simple Types
3) Types : Word [Signed]
4) Array Element : Not checked
*1: Set "Libraries", "Type Class", "Types" and "Array
Element" in this order.
After completing the setting, click the button.
(To the next page)

3 - 10
3.2.5 Setting labels
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
Refer to the following manual for the details on the global label/local label setting procedure:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Refer to the following manual for the details on programming global labels and local labels:
MELSEC-Q/L/F Structured Programming Manual (Fundamentals)
5. Directly input the "Device" on the Global Label
Setting screen.
Settings
•Device: D0
6. Set the "Constant", "Comment" and "Remark"
on the Global Label Setting screen.
"Relation with System Label", "System Label Name"
and "Attribute" are not used in examples shown in
this manual.
Settings
• Constant : When the label class is
"VAR_GLOBAL", you cannot set or
change the constant value.
• Comment : No setting
• Remark : No setting

3.2.6 Creating a program
3 - 11
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
3.2.6 Creating a program
Create the ladder program shown in Section 3.1.2.
You can select the following modes when creating a program.
• "Overwrite" mode or "Insert" mode
This section explains the creation procedure in the "Overwrite" mode.
Every time you click the key, the mode is switched between "Overwrite" and "Insert".
Select either mode as needed.
• "Write" mode or "Read" mode
Select the "Write" mode when editing the ladders.
For selecting the "Write" mode, select [Edit] [Ladder Edit Mode] [Write Mode] from the menu
bar.
Or click (Write Mode).
Refer to the following manual for details of the "Overwrite" mode, "Insert" mode, "Write" mode and
"Read" mode.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
1. Double-click "POU" "Program" "MAIN"
"Program" on the Project view to display the
[PRG] MAIN screen.
2. Click (Rising Pulse) on the Ladder toolbar
to display the Enter Symbol screen.
Directly input a device on the Enter Symbol screen,
and click the button to display the Rising
Pulse.
Settings
•X0
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

3 - 12
3.2.6 Creating a program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
Click an icon on the Ladder toolbar to open the Enter Symbol screen for inputting a device or instruction.
Set a device or instruction, and click the button to display the corresponding ladder symbol or vertical
line in the cursor position.
Ladder tool bar
Refer to the following manual for the details on the toolbar:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
3. Click (Close Contact) on the Ladder tool
bar to display the Enter Symbol screen.
Directly input a device on the Enter Symbol screen,
and click the button to display the Close
Contact.
Settings
•T0
Table 3.1 Icons on the Ladder toolbar mainly used in this section
Names Contents
Open Contact Set a device.
Close Contact
Set a device.
Rising Pulse
Set a device.
Open Branch Set a device.
Coil Set a device.
Application Instruction Input an application instruction.
Vertical Line Set the number of vertical lines.
(To the next page)

3.2.6 Creating a program
3 - 13
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
4. Click (Open Branch) on the Ladder tool bar
to display the Enter Symbol screen.
Directly input a device on the Enter Symbol screen,
and click the button to display the Open
Branch.
Settings
•Y10
5. Click (Coil) on the Ladder toolbar to display
the Enter Symbol screen.
Directly input a device on the Enter Symbol screen,
and click the button to display the Coil.
Settings
•Y10
6. Click (Vertical Line) on the Ladder toolbar
to display the Enter Vertical Line screen.
Click the button to display the Vertical Line.
7. Click (Coil) on the Ladder toolbar to display
the Enter Symbol screen.
Directly input a device and set value on the Enter
Symbol screen, and click the button to
display the Coil.
Settings
• T0 K10
8. Click (Open Contact) on the Ladder tool
bar to display the Enter Symbol screen.
Directly input a device on the Enter Symbol screen,
and click the button to display the Open
Contact.
Settings
•X1
(To the next page)

3 - 14
3.2.6 Creating a program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
9. Click (Application Instruction) on the
Ladder toolbar to display the Enter Symbol
screen.
Directly input an application instruction and operand
on the Enter Symbol screen, and click the
button to display the Application Instruction.
Settings
•MOVP K10 VAR1
*1
*1: The label VAR1 is set in Section 3.2.5.
Specify the device D0 when not using labels.
10.Click (Open Contact) on the Ladder tool
bar to display the Enter Symbol screen.
Directly input a device on the Enter Symbol screen,
and click the button to display the Open
Contact.
Settings
•X2
11.Click (Application Instruction) on the
Ladder toolbar to display the Enter Symbol
screen.
Directly input an application instruction and operand
on the Enter Symbol screen, and click the
button to display the Application Instruction.
Settings
•MOVP K20 VAR1
*2
*2: The label VAR1 is set in Section 3.2.5.
Specify the device D0 when not using labels.

3.2.6 Creating a program
3 - 15
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
Make sure to ladder conversion and compile the created or edited program to make it a sequence program
executable in the programmable controller CPU.
Only ladder conversion is required, and compilation is not required when using the FXCPU or not using labels.
Refer to the following sections for ladder conversion and compile.
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks
3.2.8 Compiling a program
If the following operation is performed after compilation, devices are displayed instead of labels.
Select [View] [Device Display] [Device Display] to check the menu item.
(Note that the menu item is unchecked when you select [View] [Device Display] [Device Display] while
the menu item is checked.)
Displaying labels and devices at the same time
Devices can be displayed at the same time in the label display mode by adding the corresponding option. Select
[Tool]
[Options] to display the Options screen. Select "Program Editor" "Ladder" "Ladder Diagram" on
the Options screen, and check "Display labels and devices".
In the example below, X1 and D0 are displayed as labels.
<Label display>
<Label/device simultaneous display>
Displaying label candidates
GX Works2 displays label candidates whose former portion agrees with the entered character string.
In this program example, GX Works2 displays labels starting from "V" when you enter "V".
You can select a displayed label instead of entering the label completely.
Devices are displayed
instead of labels.

3 - 16
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks
1. Select [Compile] [Build] to display the
Execution Confirmation for Build screen.
You can press the key instead to display the
Execution Confirmation for Build screen.
2. Set the execution method of build.
In this example, GX Works2 will convert the
selected program.
After setting the execution method, click the
button to execute conversion.
Settings
• Select "Convert the selected program".
3. [Build] converts the unconverted ladder block,
and changes its background color as shown on
the left.

3.2.8 Compiling a program
3 - 17
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.2 Creating a Project
3.2.8 Compiling a program
There are following two types of compiling. The compiling target is different between the two types.
Select "Rebuild All" for this example.
The "Rebuild All" procedure is described below.
Refer to the following manual for compiling:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Table 3.2 Compiling type and target program
Target program to be compiled
Build
Converts non-compiled programs into sequence program.
(Does not compile already compiled programs.)
Rebuild All
Converts all programs into sequence program.
(Compiles already compiled programs also.)
1. Select [Compile] [Rebuild All] to execute
"Rebuild All".
You can click (Rebuild All) to execute "Rebuild
All".
2. The screen shown on the left appears.
Click the button to execute "Rebuild All".
3. When finishing "Rebuild All", GX Works2
displays the result on the Output window.
If an error occurs, check the contents, eliminate the
cause of error, and then execute "Build" or "Rebuild
All" as described in the step 1.
4. When "Rebuild All" is completed, the number of
program steps is displayed at the window title
on the [PRG] Write MAIN screen.
When an error is not detected.

3 - 18
3.2.8 Compiling a program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
When you convert a ladder block, GX Works2 automatically compiles the program at the time of
conversion if labels are not used.
If labels are used, make sure to compile the created or edited sequence program after conversion so that
the created or edited sequence program will be an executable sequence program.
Refer to the following manual for the details on "Build", "Rebuild All":
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Compile status checking method
You can check the compile status on the Project view.
Each non-compiled portion is displayed in red.

3.3.1 Connecting the personal computer to the programmable controller
3 - 19
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
Write a project to the programmable controller CPU.
3.3.1 Connecting the personal computer to the programmable
controller
Connect the personal computer and the programmable controller with a cable, and set the connection
channel.
Connecting the personal computer to the programmable controller
For cautions on connection, refer to the manual of the programmable controller CPU.
Refer to the following manual for the details on setting when using another channel or using the FXCPU
for connection.
Setting the Transfer Setup
Set the channel to connect the personal computer to the programmable controller CPU (Q02HCPU)
with a USB cable.
Refer to the following manual for the details on setting using another channel:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
1. Click "Connection Destination" in the view
selection area on the Navigation window to
display the Connection Destination view.
2. Double-click "Connection1" in the Current
Connection on the Connection Destination view
to display the Transfer Setup screen.
programmable controller (Q02HCPU)
USB cable
Notebook personal computer
Click it.
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

3 - 20
3.3.1 Connecting the personal computer to the programmable controller
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3. Double-click (Serial USB) in "PC side I/F"
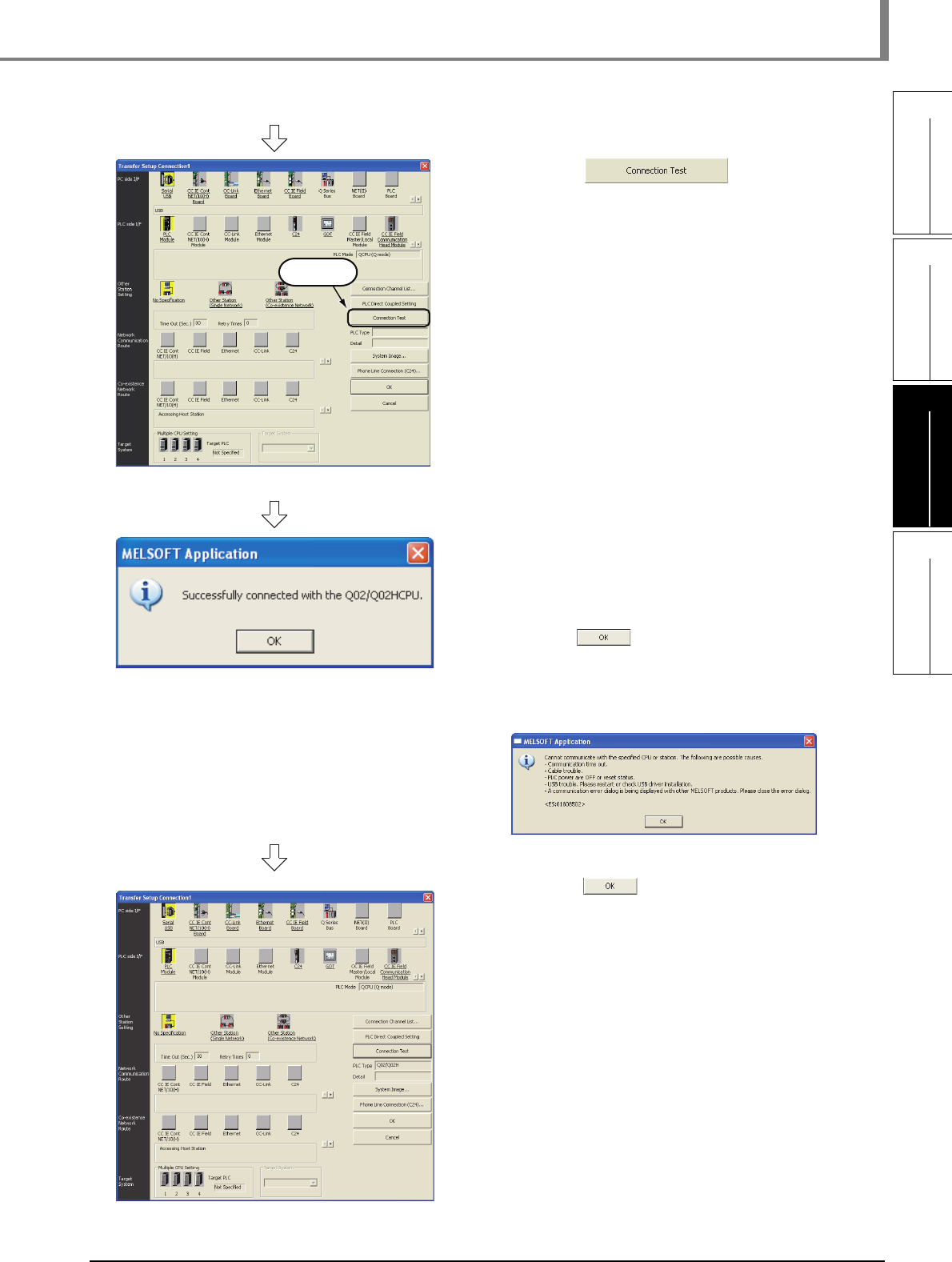
to display the PC side I/F Serial setting screen.
4. Set the PC side I/F.
After the setting, click the button to
complete the setting and close the screen.
Settings
• Select "USB".
5. Click (PLC Module) in "PLC side I/F" to
select the interface to be used.
Double-click it.
Click it.
(To the next page)
3.3.1 Connecting the personal computer to the programmable controller
3 - 21
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
6. Click the button to execute
a communication test with the programmable
controller through the specified connection
channel.
7. When communication with the programmable
controller is finished normally, the left screen
appears, and the "PLC Type" field displays the
programmable controller CPU model name.
Click the button to close the screen.
If communication with the programmable controller
has failed, the screen below appears.
Check the connection destination, connection cable,
etc.
8. Click the button to finish "Transfer
Setup" and close the screen.
Click it.

3 - 22
3.3.1 Connecting the personal computer to the programmable controller
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
You can set two or more connection destinations and change them over if there are two or more
connection destinations.
1. Select "Connection1" in the Current
Connection on the Connection
Destination view, right-click it, and then
select the menu item "Add New Data".
The Add New Data screen will appear.
2. Set "Data Name", and uncheck "Set as
Default Connection".
Click the button to display the
newly created connection destination in
"All Connections" on the Connection
Destination view.
Settings
• Data Name : Connection2
• Set as Default Connection: Unchecked
3. Set the connection destination.
Double-click "Connection2" in "All
Connections" to display the Transfer
Setup screen.
3.3.1 Step3 in the Setting the
Transfer Setup
Newly created connection destination

3.3.1 Connecting the personal computer to the programmable controller
3 - 23
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
For selecting the newly created connection destination, check "Set as Default Connection " while creating
the data, or set the newly created connection destination as the default connection destination as described
below.
Then, the newly created connection destination will be selected as the connection destination for
communication with the programmable controller CPU (for "Read from PLC", "Write to PLC", etc).
1. Select "Connection2" in the All
Connections on the Connection
Destination view, right-click it, and then
select the menu item "Set as Default
Connection".
2. The connection destination set as the
default connection destination is
displayed in "Current Connection" on
the Connection Destination view.
Default Connection

3 - 24
3.3.2 Writing a project to the programmable controller
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.3.2 Writing a project to the programmable controller
Write the project data to the programmable controller CPU set as the connection destination in Section
3.3.1.
1. Select "Online" "Write to PLC" to display the
Online Data Operation screen.
You can click (Write to PLC) to display the Online
Data Operation screen.
2. Set the "Target module" and "Target project" on
the Online Data Operation screen.
After the setting, click the button.
Setting of the target module
• Target module: Select <<PLC Module>>
Setting of the project
• Symbolic Information : Select "Program Memory/Device Memory" in "Target Memory", and
check "Symbolic Information" in "Target".
"Program (Program File)" and "MAIN" are checked in "PLC Data", and
change into gray.
"Symbolic Information" contains program files and variables.
• PLC Data : Select "Program Memory/Device Memory" in "Target Memory", and
check "PLC/Network/Remote Password/Switch Setting" in "Target". Do
not check "Global Device Comment" or "Device Memory".
Setting of the target module
Click it.
Setting of the project
(To the next page)

3.3.2 Writing a project to the programmable controller
3 - 25
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
Restrictions
In the case of FXCPU
• The symbolic information is displayed only in the FX
3U and FX3UC Series version 3.00 or later.
• In the case of Simple project (with labels), data can be read from the FXCPU only in the FX
3U and FX3UC Series
version 3.00 or later.
When data cannot be read from the FXCPU, carefully store projects written in the programmable controller.
3. The left screen is displayed.
Click the button to
write the project (program).
If a program or parameters already exist in the programmable controller, the following screen appears.
Click the or button to overwrite the existing program or parameters.
When you click the button, GX Works2 overwrite the existing program or parameters without
displaying the overwrites confirmation screen for other data.
4. The left screen is displayed during
writing.
When writing is finished, "Write to
PLC: Completed" appears.
Click the button to close the
Write to PLC screen.
When parameters already exist When a program already exists
Writing Completed
(To the next page)

3 - 26
3.3.2 Writing a project to the programmable controller
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
5. Click the button to close the
Online Data Operation screen.

3.4.1 Monitoring a program
3 - 27
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.4 Monitoring Operations
3.4 Monitoring Operations
Execute "Monitor" to check the operations.
GX Works2 is able to simulate the programmable controller operations in offline mode.
Refer to the following manual for the simulation function:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
3.4.1 Monitoring a program
1. Click "Project" in the view selection area on the
Navigation window to display the Project view.
2. Double-click "POU" "Program" "MAIN"
"Program" on the Project view to display the
[PRG] MAIN screen.
3. Select [Online] [Monitor] [Monitor Mode]
to switch the [PRG] MAIN screen to the
monitoring status.
You can also click (Monitor Mode) to switch the
[PRG] MAIN screen to the monitoring status.
4. Set the programmable controller CPU to RUN.
Set the RUN/STOP switch on the programmable
controller CPU to "RUN".
Click it.
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

3 - 28
3.4.1 Monitoring a program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
You can switch the programmable controller status between "RUN" and "STOP" using remote operation as
follows.
The Settings of the remote operation may vary depending on the programmable controller used.
Refer to the following manual for the details on remote operation:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
Select [Online] [Remote Operation] to display the Remote Operation screen. You can switch the
programmable controller status between "RUN" and "STOP" on this screen.
Monitor status display example
Operation
Allows you to select the
programmable controller
CPU status to be set.
Select either "RUN",
"PAUSE" or "STOP" for
this example.
Programmable
controller Status
Displays the
programmable controller
CPU status.
Connection Channel
List information
Displays the connection
target information
currently set.
Specify Execution
Target
Allows you to set the
target station for
remote operation.
Select "Currently
Specified Station" for
this example.
Operation during RUN
Allows you to set the
operations to be
executed to the device
memory and signal flow
when the
programmable
controller CPU is
switched to RUN.
Displays the ON status.
Displays the current values.
(To the next page)

3.4.1 Monitoring a program
3 - 29
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.4 Monitoring Operations
Monitor status
GX Works2 displays the Monitor status while it is executing the work window monitor.
The Monitor status disappears when GX Works2 stops all types of monitoring.
The Monitor status indicates the programmable controller CPU, simulator scan time, RUN/STOP status, etc.
Refer to the following manual for the details on "Monitor status":
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
Monitor status display
ON/OFF status display
GX Works2 displays the ON/OFF status as follows during monitoring.
* GX Works2 adopts this display method only for the SET, RST, PLS, PLF, SFT, SFTP and MC
instructions and contact type comparison instructions.
As to monitoring of the RST instruction, GX Works2 displays the ON/OFF status of a reset
device.
Current value display
GX Works2 displays the monitored current value as follows.
Switching of the current value display between decimal and hexadecimal
You can switch the current value display between decimal and hexadecimal using the following operations.
Operation to switch the current value display to decimal
Select [Online] [Monitor] [Change Value Format (Decimal)].
Operation to switch the current value display to hexadecimal
Select [Online] [Monitor] [Change Value Format (Hexadecimal)].
Refer to the next page for the test operation.
Scan status
Select the Local Device monito
r
USER status
ERR. status
RUN/STOP status
Connection status
*
*
OFF status
ON status
Current value of T0 Current value of VAR1

3 - 30
3.4.1 Monitoring a program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
Test operation
Forcing a contact ON/OFF
Double-click ( ) a monitored contact while pressing the key to force a device in the
programmable controller ON/OFF.
Changing the current value of a word device
Double-click ( ) a monitored word device while pressing the key to display the Modify Value
screen where you can change the current value.
5. Turn ON inputs X0, X1 and X2 in the programmable controller, and check the following
operations.
You can turn ON inputs X0, X1 and X2 using the test operation above.
• When X0 turns ON, the programmable controller turns ON Y10, and then turns OFF Y10 1
second later.
• When X1 turns ON, the programmable controller transfers K10 to VAR1 (device: D0).
• When X2 turns ON, the programmable controller transfers K20 to VAR1 (device: D0).
Input the numeric value to be set, and
click the button to change the
current value to the input numeric value.
X0 turns ON.
It turns OFF 1 second later.
The programmable controller turns ON Y10.
X1 turns ON.
The programmable controller transfers K10 to VAR1.
X2 turns ON.
The programmable controller transfers K20 to VAR1.
(To the next page)

3.4.1 Monitoring a program
3 - 31
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.4 Monitoring Operations
6. Select [Online] [Monitor] [
Stop Monitoring
]
to reset the monitor status of the [PRG] MAIN
screen.
You can click (Stop Monitoring) to reset the
monitor status of the [PRG] MAIN screen.
7. Set the programmable controller CPU to STOP.
Set the RUN/STOP switch on the programmable controller CPU to "STOP".
You can switch the programmable controller status between "RUN" and "STOP" using remote
operation.
For the remote operation, refer to the following.
"Point" in the step 4
Switch the programmable controller CPU to the "Write" mode when editing the ladders.
Refer to the following manual for details of the "Overwrite" mode, "Insert" mode, "Write" mode and
"Read" mode.
3.2.6 Creating a program

3 - 32
3.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
1. Select [Online] [Monitor] [Device/Buffer
Memory Batch] to display the Device/Buffer
Memory Batch Monitor screen.
Or click (Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor)
to display the Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor
screen.
2. Set a device to be monitored.
Select D0 in this example.
Setting of "Device"
• Device : Select "Device Name".
• Device Name : D0
3. Click the button to display the Display
Format screen.
Setting
Restrictions
Set a device name to be monitored.
Label Name is not available.
(To the next page)

3.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
3 - 33
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.4 Monitoring Operations
4. Set the Display Format of the device to be
monitored.
Setting on the Display Format screen
• Monitor Format : Bit and Word
• Display : 16 bit Integer
• Value : DEC
• Bit Order : 0-F
• Switch No. of Points : Bit Device Bit and Word
Format 16 Points
Word Device Word Multi-
point Format 8 Points
After the setting, click the button to close
the Display Format screen.
Refer to the following manual for the details on
Display Format.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual
(Common)
5. Click (Start Monitoring) on the Ladder
toolbar to start monitoring.
6. Set the programmable controller CPU to RUN.
Set the RUN/STOP switch on the programmable
controller CPU to "RUN".
You can save the contents set on the Display Format screen.
When the monitoring screen is opened again, the contents set previously on the "Display
Format" screen will not be displayed. (The default setting will be displayed.) To display the
previous setting, you can save the setting to a file, and read the file. To save the setting, click
button on the Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor screen. To read the saved setting,
click button on the Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor screen.
You can set the data display format also on the Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor screen.
For setting the display format, click the "Display Format" button on the Device/Buffer Memory
Batch Monitor screen.
The contents of setting are reflected on the Display Format screen.
(To the next page)

3 - 34
3.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
7. Click (Stop Monitoring) on the Ladder
toolbar to stop monitoring.
Monitored values remain even after GX Works2
stops monitoring.
8. Click on the screen to close the Device/
Buffer Memory Batch Monitor screen.
9. Set the programmable controller CPU to STOP.
Set the RUN/STOP switch on the programmable
controller CPU to "STOP".
You can switch the programmable controller status
between "RUN" and "STOP" using remote
operation.
For the remote operation, refer to the following.
"Point" in the 3.4.1
Opening two or more Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor screens
You can open two or more Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor screens.
The screen number is indicated at the end of the screen title.
Current value
Click it.
Number
(To the next page)

3.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
3 - 35
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.4 Monitoring Operations
Changing the current value
Click the button on the Device/Buffer Memory Batch Monitor screen to display the Modify
Value screen which allows you to change the current value.
1. Select a device whose current
value is to be changed.
2. Click the button to
display the Modify Value screen.
Or click (Modify Value) to display
the Modify Value screen.
3. Change the current value.
For the change procedure, refer to
the following.
"Point" in the 3.4.1
Selecting
Click it.
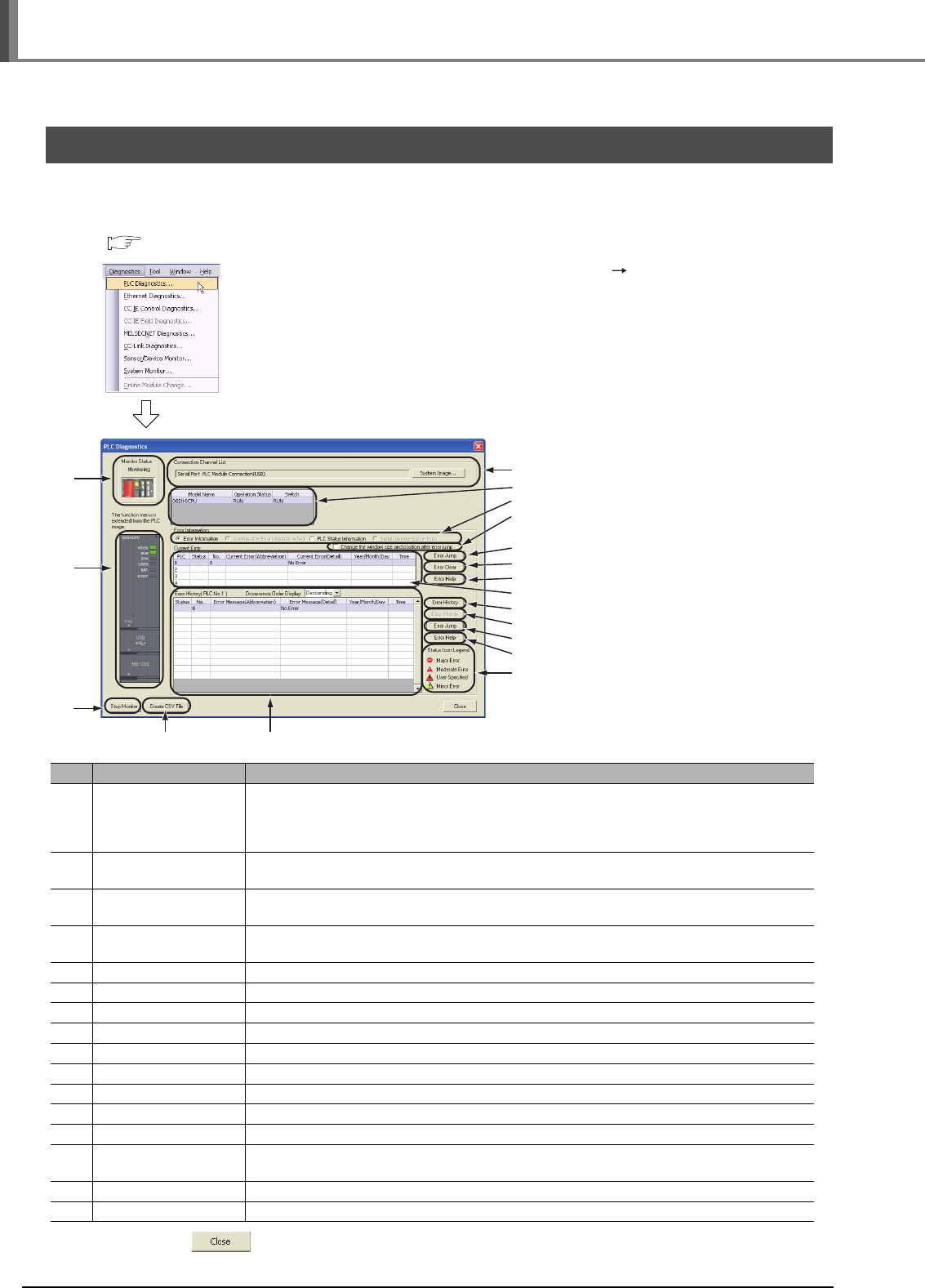
3 - 36
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.5 Diagnosing the programmable controller
You can check the programmable controller RUN/STOP status and error status.
Refer to the following manual for the details on Network Diagnostics, Ethernet Diagnostics and CC-Link IE
Control Diagnostics.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
1. Select [Diagnostics] [PLC Diagnostics] to
display the PLC Diagnostics screen.
2. Click the button to close the PLC Diagnostics screen.
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
7)
9)
12)
6)
13)
14)
15)
16)
No. Item Description
1) Connection Channel List
Connection Channel List:
Displays the information on connection between the personal computer and the programmable
controller CPU.
System Image: Displays visually the Connection Channel List.
2)
CPU information of
connected station
Displays the model name, operation status and switch status.
3)
Displayed information
selection
Select a radio button to display Error Information (Current Error and Error History)/Continuation
Error Information/PLC Status Information/Serial Communication Error.
4) Setting for Error Jump
Check this check box to reduce the PLC Diagnostics screen size and adjust the display position
at the time of Error Jump.
5) Current Error Displays the current CPU error information.
6) Error History Displays the error history.
7) Error Jump
Jumps to the ladder step number which contains the error corresponding to the currently selected error number.
8) Error Clear Clears the error information displayed in "Current Error".
9) Error Help Displays the explanation window for the currently selected error number.
10) Error History Displays the latest error history.
11) Clear History Deletes the error history list in "Error History".
12) Status Icon Legend
Indicates icons corresponding to errors displayed in the "Status" column of the "Error Information".
13) Monitor Status Indicates the monitoring status (executed or stopped).
14)
Programmable controller
CPU information
Displays the programmable controller CPU status.
15) Stop Monitor Starts or stops monitoring.
16) Create CSV File Saves the error information to a CSV file.

3 - 37
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller
3.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller
You can read data to a project from the programmable controller CPU selected as the connection destination
in Section 3.3.1.
1. Select [Online] [Read from PLC]
to display the Online Data Operation
screen.
You can click (Read from PLC) to
display the Online Data Operation
screen.
2. Set the "Target module" and "Target
project" on the Online Data
Operation screen.
After the setting, click the
button to read the project (program)
from the programmable controller.
Setting of the target module
• Target module: Select <<PLC Module>>.
Setting of the project
• Symbolic Information : Select "Program Memory/Device Memory" in "Target Memory", and
check "GX Works2 (Simple Project)" in "Target".
"Symbolic Information" contains program files and variables.
• PLC Data : Select "Program Memory/Device Memory" in "Target Memory", and
check "PLC/Network/Remote Password/Switch Setting" in "Target".
*1
Do not check "Global Device Comment" and "Device Memory".
*1: If you have checked desired items for the Write to PLC setting, such items are checked as the
default for the Read from PLC setting.
Check the following when not using labels:
• Program (program file)
• Parameter
Setting of the target module
Click it.
Setting of the project
Restrictions
In the case of FXCPU
• When labels are used, data can be read from the FXCPU only in the FX
3U and FX3UC Series version 3.00 or later.
When data cannot be read from the FXCPU, carefully store projects written in the programmable controller.

3 - 38
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
If a program or parameters already exist in the GX Works2, the following screen appears.
Click the or button to overwrite the existing program or parameters.
When you click the button, GX Works2 overwrite the existing program or parameters without
displaying the overwrites confirmation screen for other data.
3. The left screen is displayed during
reading.
When reading is finished, "Read from
PLC: Completed" appears.
Click the button to close the
Read from PLC screen.
4. Click the button to close the
Online Data Operation screen.
When symbolic information already exists When parameters already exist
Reading Completed

3.7.1 Setting the printer
3 - 39
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.7 Printing
3.7 Printing
You can print programs and parameters created using GX Works2 in a printer.
The print function consists of Batch print and print. This section explains print.
For details of printing, refer to the following manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
3.7.1 Setting the printer
The printer which prints is set up.
1. Select [Project] [Printer Setup] to display the
Printer Setup screen.
2. Select the Printer, Paper size, Orientation, etc.
After the setting, click the button to close
the Printer Setup screen.

3 - 40
3.7.2 Previewing a program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.7.2 Previewing a program
You can display a program in the image of printing.
1. Click "Project" in the view selection area on the
Navigation window to display the Project view.
2. Display a program.
Double-click "POU" "Program" "MAIN"
"Program" on the Project view to display the [PRG]
MAIN screen.
3. Select [Project] [Print Window Preview] to
display the Print Window Preview (Ladder)
screen.
Click it.
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

3.7.2 Previewing a program
3 - 41
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.7 Printing
4. Click the button to determine the
setting and display the Print Window Preview
screen.
In this example, the Print Window Preview (Ladder)
screen remains in the initial setting.
For details of the setting on the Print Window
Preview (Ladder) screen, refer to the following
manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual
(Common)
5. After checking the contents, click the button to print the program.
Click the button to close the Print Window Preview screen.
Click it.
Click button to print the program.

3 - 42
3.7.3 Printing a program
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.7.3 Printing a program
1. Display a program.
For the display procedure, refer to the following.
3.7.2 Previewing a program
2. Select [Project] [Print Window] to display the
Print Window (Ladder) screen.
3. Click the button to determine the
setting and start printing.
In this example, the Print Window (Ladder) screen
remains in the initial setting.
For details of the setting on the Print Window
(Ladder) screen, refer to the following manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual
(Common)
Click it.

3.7.4 Previewing a PLC Parameter
3 - 43
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.7 Printing
3.7.4 Previewing a PLC Parameter
You can display PLC Parameter in the image of printing.
1. Display PLC parameters.
Double-click "Parameter" "PLC Parameter" on
the Project view to display the Q Parameter Setting
screen.
2. Click the button.
3. After checking the contents, click the
button to print PLC Parameter.
Click the button to close the Print Window
Preview screen.
Double-click it.
Click it.
Click button to print PLC
Parameter.

3 - 45
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
3.8 Saving a Project
3.8 Saving a Project
You can save a project.
When saving a newly created project, use the menu item [Save as].
1. Select [Project] [Save As] to display the
Save As screen.
2. Set "Save Location", "Workspace Name",
"Project Name", "Title", etc.
After the setting, click the button to save the
project (program).
Refer to the following manual for the details:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual
(Common)
Settings
Restrictions
Input within 128 characters to "Title".
Make sure that the total characters of "Save Folder Path", "Workspace Name" and "Project Name" is 200
or less.
You cannot save any project to route directories such as "C:\" or "D:\".
• Save in : Specify the save destination
folder.
• File name : Specify the file name.
• Title : Specify the title.
You can save a project without
specifying a title.

3 - 46
3 CREATING A PROGRAM OF LADDER
3.9 Exiting GX Works2
End the project.
1. Select [Project] [Exit (Q)] to exit GX Works2.
If you have not saved the project, the following message appears.
Click the button to save the project.
Click the button to exit GX Works2 without saving the project.

4 - 1
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF
SFC
This chapter explains how to create a program of SFC with a Simple Project through a simple program
example.
4.1 Created Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.2 Created Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller . . . . . . . . . 4-27
4.4 Monitoring Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-27
4.5 Diagnosing the programmable controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30
4.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller . . . . . . . . . 4-30
4.7 Printing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30
4.8 Saving a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30
4.9 Exiting GX Works2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-30

4 - 2
4.1.1 Operations of program
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
4.1 Created Program
This section explains the operations of the program to be created and SFC programs.
4.1.1 Operations of program
This program controls fountain (cycle operation/continuous operation).
Cycle operation (when X1 is OFF)
When the start button (X0) is pressed, the program will make progress in the sequence "Standby
status (S0) Center lamp (S1) Center fountain (S2) Loop line lamp (S3) Loop line
fountain (S4) Standby status (S0)".
Each output is switched by the timer at every 2 seconds.
Continuous operation (when X1 is ON)
When the start button (X0) is pressed, the program will make progress in the sequence "Standby
status (S0) Center lamp (S1) Center fountain (S2) Loop line lamp (S3) Loop line
fountain (S4) Center lamp (S1)", and then repeat this sequence.
Each output is switched by the timer at every 2 seconds.
3
Mode selection
Start Standby
Programmable controller output assignment
Y010: Standby indication
Y011: Center lamp
Y012: Center fountain
Y013: Loop line lamp
Y017: Loop line fountain

4.1.2 Created Program
4 - 3
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.1 Created Program
4.1.2 Created Program
For QCPU/LCPU
For FXCPU
4 - 4
4.2.1 Starting GX Works2
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
Create a project using SFC programs.
4.2.1 Starting GX Works2
For the GX Works2 starting procedure, refer to the following.
3.2.1 Starting GX Works2
4.2.2 Screen configuration in GX Works2
For the GX Works2 screen configuration, refer to the following.
3.2.2 Screen configuration in GX Works2
4.2.3 Creating a new project
For the new project creating procedure, refer to the following.
Select SFC as the "programming language".
3.2.3 Creating a new project
4.2.4 Setting parameters
For the Parameter setting procedure, refer to the following.
3.2.4 Setting parameters
Refer to the following manuals for the details on Setting parameters.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
CPU manual
CPU programming manual
Perform the following when using the FXCPU:
Uncheck "Use Label".
The FXCPU does not support the Label in SFC language.
If it is checked, SFC is not selectable as the "Language".
When you select SFC as the "Language" and create a new project, the Block Information Setting screen
appears.
Refer to the following for the setting procedure.
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)

4.2.5 Setting labels (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 - 5
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
4.2.5 Setting labels (for QCPU/LCPU)
For the Global Label setting procedure, refer to the following.
3.2.5 Setting labels
For details of the Global Label and Local Label setting procedures, refer to the following manual.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Setting on the Global Label
Restrictions
The FXCPU does not support the Label in SFC language.
Directly input a device.

4 - 6
4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
Create the SFC program (for QCPU/LCPU) shown in Section 4.1.2.
You can select the following modes when creating a program.
• "Overwrite" mode or "Insert" mode
• "Write" mode or "Read" mode
Refer to the following manual for details of the "Overwrite" mode, "Insert" mode, "Write" mode and
"Read" mode.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
1. Double-click "POU" "Program" "MAIN"
"000: Block" "Program" on the Project
view to display the SFC screen for "[PRG] 000:
Block".
SFC diagram/Zoom screen layout
By setting "Options", the SFC diagram and Zoom screen can be displayed together vertically or
horizontally.
Select [Tool] [Options] to display the Options screen.
On the Options screen, select "Program Editor" "SFC" "SFC 1" "Arrange Windows for
MELSAP3" "Arrange", and set the following.
Settings
• Tile SFC and Zoom vertically: Check it.
• Arrange: Select "Tile Horizontally" or "Tile Vertically".
Change the position or size of the window to change over the SFC diagram/Zoom screen layout.
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 - 7
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
2. Creating the SFC Diagram (step 0)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 1,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-
click it to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting the items, click the button to
move the cursor to the next row.
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/0
• Step Attribute : [--]
• Comment : Standby status
3. Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 0)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 2,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-
click it to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting the items, click the button to
move the cursor to the next row.
Settings
•Symbol : TR/0
• Comment : blank
4. Creating the SFC Diagram (step 1)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 4, column
number 1".
"Step2" in the 4.2.6
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/1
• Step Attribute : [--]
• Comment : Center lamp
5. Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 1)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 5, column
number 1".
"Step3" in the 4.2.6
Settings
•Symbol : TR/1
• Comment : blank
(To the next page)

4 - 8
4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
6. Creating the SFC Diagram (step 2)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 7, column
number 1".
"Step2" in the 4.2.6
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/2
• Step Attribute : [--]
• Comment : Center fountain
7. Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 2)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 8, column
number 1".
"Step3" in the 4.2.6
Settings
• Symbol : TR/2
• Comment : blank
8. Creating the SFC Diagram (step 3)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 10,
column number 1".
"Step2" in the 4.2.6
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/3
• Step Attribute : [--]
• Comment : Loop line lamp
9. Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 3)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 11,
column number 1".
"Step3" in the 4.2.6
Settings
• Symbol : TR/3
• Comment : blank
(To the next page)

4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 - 9
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
10.Creating the SFC Diagram (step 4)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 13,
column number 1".
"Step2" in the 4.2.6
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/4
• Step Attribute : [--]
• Comment : Loop line fountain
11.Creating the SFC Diagram (Selective branch)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 14,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-click it
to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting the items, click the button to
move the cursor to the next row.
Settings
•Symbol : --D/1
12.Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 4)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 15,
column number 1".
"Step3" in the 4.2.6
Settings
•Symbol : TR/4
• Comment : blank
13.Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 5)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 15,
column number 2".
"Step3" in the 4.2.6
Settings
•Symbol : TR/5
• Comment : blank
(To the next page)

4 - 10
4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
14.Creating the SFC Diagram (Jump to the
Continuous operation)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 16,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-click it
to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting "Symbol", click the button to
display the jump destination step number.
Settings
• Symbol : JUMP/1
15.Creating the SFC Diagram (jump to the Cycle
operation)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 16,
column number 2" on the screen, and double-click it
to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting "Symbol", click the button to
display the jump destination step number.
Settings
• Symbol : JUMP/0
(To the next page)

4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 - 11
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
The step ( ) specified as the jump destination will change into ()
Perform the following procedure to display comments set on the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
Select [View] [SFC Step/Transition Comment].
16.Creating the zoom (operation output of the step
0)
Put the cursor in the zoom block (such as step and
serial transition), and then perform the following
procedure to display the zoom.
In this case, put the cursor in the step 0.
Select [View] [Open Zoom/Start Destination
Block].
Perform the following to return to the SFC screen:
Select [View] [Back to Zoom SFC Block].
Create the operation output of the step 0 (standby
status), and convert the ladder.
For operation output creation and ladder conversion,
refer to the following.
3.2.6 Creating a program
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks
(To the next page)

4 - 12
4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
The step ( ) whose operation output is created will change into ()
17.Creating the zoom (Transition condition of
series transition 0)
Display the zoom.
For the display method, refer to the following.
"Step16" in the 4.2.6
For operation output creation and ladder conversion,
refer to the following.
3.2.6 Creating a program
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks
(To the next page)

4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 - 13
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
In the transition condition, the coil instruction accepts only one dummy coil ([TRAN]).
Click " " or " ", and click the button to enter the dummy coil. Then, "[TRAN]" will be entered
automatically.
18.Creating the zoom (step1, series transition 1, step2, series transition 2, step3, series
transition 3, step4, series transition 4, series transition 5)
For the zoom display and creation methods, refer to the following.
"Step16" in the 4.2.6
"Step17" in the 4.2.6
"Point" in the Step17
(To the next page)

4 - 14
4.2.6 Creating a program (for QCPU/LCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC

4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 - 15
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
Create the SFC program (for FXCPU) shown in Section 4.1.2
You can select the following modes when creating a program.
• "Overwrite" mode or "Insert" mode
• "Write" mode or "Read" mode
Refer to the following manual for details of the "Overwrite" mode, "Insert" mode, "Write" mode and
"Read" mode.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
When you select "SFC" as the "Language" for creating a new project, the Block Information Setting
screen appears.
1.
Creating a ladder block.
Set "Title" and "Block Type".
After setting, click the button to
close the Block Information Setting screen
and add "000: Block Starting ladder"
(ladder block) on the Project view screen.
"SFC Block" and "Ladder Block" can be
selected as the "Block Type".
When the FXCPU is used, it is necessary to
create a ladder for turning ON the SFC
program using a ladder block.
Settings
• Title : Starting ladder
• Block Type : Ladder Block
2. Creating the SFC Block
Select "MAIN" on the Project view
screen, right-click it, and then select the
menu item "Add New Data".
The New Data screen will appear.
Added.
(To the next page)

4 - 16
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
3. Creating the SFC Block
Set "Data Type" and "Language".
Leave "Data Name" in the initial setting
(Block1). After setting, click the
button to close the New Data
screen and display the Block
Information Setting screen.
Settings
• Data Type : Program
• Language : SFC
4. Creating the SFC Block
Set "Title" and "Block Type".
After setting, click the button to
close the Block Information Setting
screen and add "001: Block1 Fountain
control" (SFC block) on the Project
view screen.
When using the FXCPU, create an SFC
program in this block.
Set to ON the initial step of this block using
the ladder block created in "000: Block".
Settings
• Title : Fountain control
• Block Type : SFC Block
5. Creating the SFC Diagram
Double-click "POU" "Program"
"MAIN" "001: Block1 Fountain
control" on the Project view to display
the SFC screen for "[PRG] 001: Block1
Fountain control".
Added.
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 - 17
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
SFC diagram/Zoom screen layout
By setting "Options", the SFC diagram and Zoom screen can be displayed together vertically or
horizontally.
Select [Tool] [Options] to display the Options screen.
On the Options screen, select "Program Editor" "SFC" "SFC 1" "Arrange Windows for
MELSAP3" "Arrange", and set the following.
Settings
• Tile SFC and Zoom vertically: Check it.
• Arrange: Select "Tile Horizontally" or "Tile Vertically".
Change the position or size of the window to change over the SFC diagram/Zoom screen layout.
6. Creating the SFC Diagram (step 0)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 1,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-
click it to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting the items, click the button to
move the cursor to the next row.
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/0
• Comment : Standby status
7. Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 0)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 2,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-
click it to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting the items, click the button to
move the cursor to the next row.
Settings
•Symbol : TR/0
(To the next page)

4 - 18
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
8. Creating the SFC Diagram (step 10)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 4,
column number 1".
"Step6" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/10
• Comment : Center lamp
9. Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 1)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 5, column
number 1".
"Step7" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : TR/1
10.Creating the SFC Diagram (step 11)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 7, column
number 1".
"Step6" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/11
• Comment : Center fountain
11.Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 2)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 8, column
number 1".
"Step7" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : TR/2
Restrictions
When using the FXCPU, set steps of the SFC program as follows:
• States S0 to S9 are called initial steps (states), and used only as head step numbers of SFC blocks.
Accordingly, you can create up to 10 SFC blocks (starting from S0 to S9) when using the FXCPU.
• States S10 and later can be used as general step numbers. However, note that the maximum
number of steps in 1 block is 512.
• Each step (state) number can be used only once throughout all blocks.
(To the next page)

4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 - 19
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
12.Creating the SFC Diagram (step 12)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 10,
column number 1".
"Step6" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/12
• Comment : Loop line lamp
13.Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 3)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 11,
column number 1".
"Step7" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : TR/3
14.Creating the SFC Diagram (step 13)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 13,
column number 1".
"Step6" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : STEP/13
• Comment : Loop line fountain
15.Creating the SFC Diagram (Selective branch)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 14,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-click it
to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting the items, click the button to
move the cursor to the next row.
Settings
• Symbol : --D/1
16.Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 4)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 15,
column number 1".
"Step7" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : TR/4
(To the next page)

4 - 20
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
17.Creating the SFC Diagram (Series transition 5)
For the creation method, refer to the following.
Put the cursor in the position "row number 15,
column number 2".
"Step7" in the 4.2.7
Settings
• Symbol : TR/5
18.Creating the SFC Diagram (Jump to the
Continuous operation)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 16,
column number 1" on the screen, and double-click it
to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting "Symbol", click the button to
display the jump destination step number.
Settings
• Symbol : JUMP/1
• Step Attribute : [--]
19.Creating the SFC Diagram (jump to the Cycle
operation)
Put the cursor in the position "row number 16,
column number 2" on the screen, and double-click it
to display the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
After setting "Symbol", click the button to
display the jump destination step number.
Settings
• Symbol : JUMP/0
• Step Attribute : [--]
(To the next page)

4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 - 21
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
The step ( ) specified as the jump destination will change into ( ).
Perform the following procedure to display comments set on the Enter SFC Symbol screen.
Select [View] [SFC Step/Transition Comment].
(To the next page)

4 - 22
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
20.
Creating the zoom (operation output of the step 0)
Put the cursor in the zoom block (such as step and
serial transition), and then perform the following
procedure to display the zoom. In this case, put the
cursor in the step 0.
Select [View]
[Open Zoom/Start Destination
Block].
Perform the following to return to the SFC screen:
Select [View]
[Back to Zoom SFC Block].
Create the operation output of the step 0 (standby
status), and convert the ladder.
For operation output creation and ladder conversion,
refer to the following.
3.2.6 Creating a program
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks
The step ( ) whose operation output is created will change into ().
(To the next page)

4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 - 23
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
21.Creating the zoom (Transition condition of
series transition 0)
Display the zoom.
For the display method, refer to the following.
"Step20" in the 4.2.7
For operation output creation and ladder conversion,
refer to the following.
3.2.6 Creating a program
3.2.7 Converting ladder blocks
In the transition condition, the coil instruction accepts only one dummy coil ([TRAN]).
Click " " or " ", and click the
button to enter the dummy coil. Then, "[TRAN]" will be entered
automatically.
22.Creating the zoom (step10, series transition 1, step11, series transition 2, step12, series
transition 3, step13, series transition 4, series transition 5)
For the zoom display and creation methods, refer to the following.
"Step20" in the 4.2.7
"Step21" in the 4.2.7
"Point" in the Step21
(To the next page)

4 - 24
4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
(To the next page)

4.2.7 Creating a program (for FXCPU)
4 - 25
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2 Created Program
23.When the FXCPU is used, it is necessary to create a ladder for turning ON the SFC
program using a ladder block. Double-click "000: Block Starting ladder", and create a
necessary circuit.
In this example, the initial state S0 is set to ON using the special auxiliary relay M8002 that is
actuated instantaneously when the programmable controller mode is changed from STOP to RUN.

4 - 26
4.2.8 Compiling a program (for QCPU/LCPU) or converting an SFC diagram (for FXCPU)
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
4.2.8 Compiling a program (for QCPU/LCPU) or converting an SFC
diagram (for FXCPU)
Compiling a program (QCPU/LCPU)
For the program compiling procedure, refer to the following.
3.2.8 Compiling a program
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Simple Project)
Convert an SFC diagram (FXCPU)
Select [View] [Back to Zoom SFC Block] to return to the SFC screen, and convert an SFC diagram.
• Select [Compile] [Build] to execute
conversion.

4.4.1 Monitoring a program
4 - 27
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
4.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
For writing a project to the programmable controller CPU, refer to the following.
3.3 Writing a Project to the programmable controller
4.4 Monitoring Operations
Execute "Monitor" to check the operations.
GX Works2 is able to simulate the programmable controller operation in offline mode.
Refer to the following manual for the simulation function.
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
4.4.1 Monitoring a program
1. Click "Project" in the view selection area on the
Navigation window to display the Project view.
2. Double-click "POU" "Program" "MAIN"
"000: Block" "Program" on the Project view
screen to display the SFC screen for "[PRG]
000: Block".
When using the FX CPU, double-click "001:
Block1 Fountain control".
3. Select [Online] [Monitor] [Monitor Mode] to
switch the [PRG] 000: Block screen to the
monitoring status.
You can also click (Monitor Mode) to switch the
[PRG] 000: Block screen to the monitoring status.
4. Set the programmable controller CPU to RUN.
Set the RUN/STOP switch on the programmable
controller CPU to "RUN".
Click it.
Double-click it.
(To the next page)

4 - 28
4.4.1 Monitoring a program
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
You can switch the programmable controller status between "RUN" and "STOP" using remote operation as
follows.
The Settings of the remote operation may vary depending on the programmable controller CPU used.
Refer to the following manual for the details on remote operation:
GX Works2 Version 1 Operating Manual (Common)
Select [Online] [Remote Operation] to display the Remote Operation screen. You can switch the
programmable controller status between "RUN" and "STOP" on this screen.
Operation
Allows you to select the
programmable controller
CPU status to be set.
Select either "RUN",
"PAUSE" or "STOP" for
this example.
Programmable
controller Status
Displays the
programmable controller
CPU status.
Connection Channel
List information
Displays the connection
target information
currently set.
Specify Execution
Target
Allows you to set the
target station for
remote operation.
Select "Currently
Specified Station" for
this example.
Operation during RUN
Allows you to set the
operations to be
executed to the device
memory and signal flow
when the
programmable
controller CPU is
switched to RUN.
(To the next page)

4.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
4 - 29
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.4 Monitoring Operations
4.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
For the Batch monitoring of device values procedure, refer to the following.
3.4.2 Batch monitoring of device values
Monitor status display example
5. Select [Online] [Monitor] [
Stop Monitoring
]
to reset the [PRG] 000: Block screen.
You can click (Stop Monitoring) to reset the
monitor status of the [PRG] MAIN screen.
6. Set the programmable controller CPU to STOP.
Set the RUN/STOP switch on the programmable
controller CPU to "STOP" using remote operation.
You can switch the programmable controller CPU
status "RUN" and "STOP" using remote operation.
For the remote operation, refer to the following.
"Point" in the step4
Switch the programmable controller CPU to the
"Write" mode when editing the SFC programs.
Refer to the following manual for details of the
"Overwrite" mode, "Insert" mode, "Write" mode and
"Read" mode.
3.2.6 Creating a program
Active step
Inactive step
(Blue)
: Active step
: Inactive step

4 - 30
4 CREATING A PROGRAM OF SFC
4.5 Diagnosing the programmable controller
You can check the programmable controller RUN/STOP status and error status.
Refer to the following section for the diagnosis procedure:
3.5 Diagnosing the programmable controller
4.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller
Refer to the following section for the procedure to read a project from the programmable controller:
3.6 Reading a Project from programmable controller
4.7 Printing
For the Printing a project procedure, refer to the following.
3.7 Printing
There are following differences in the case of SFC programs.
• Previewing a program: The Print Window Preview (Ladder) screen is not displayed.
• Printing a program : The Print Window screen is displayed.
4.8 Saving a Project
For the Saving a Project procedure, refer to the following.
3.8 Saving a Project
4.9 Exiting GX Works2
Refer to the following section for the project ending procedure:
3.9 Exiting GX Works2

4 - 31
1
OVERVIEW
2
CREATED PROGRAM
AND SYSTEM
CONFIGURATION
3
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF
LADDER
4
CREATING A
PROGRAM OF SFC
4.9 Exiting GX Works2
MEMO

TRADEMARKS
Windows is a trademark of the Microsoft group of companies.
The company names, system names and product names mentioned in this manual are either registered trademarks or
trademarks of their respective companies.
In some cases, trademark symbols such as '
' or '
' are not specified in this manual.
COPYRIGHTS
SPREAD
Copyright 2004 FarPoint Technologies, Inc.
VS-FlexGrid Pro 8.0J
Copyright 2001-2003 ComponentOne LLC.

SH(NA)-080787ENG-T(2306)KWIX
MODEL: GXW2-HOW-O-SP-E
MODEL CODE: 13JZ22
Specifications subject to change without notice.
When exported from Japan, this manual does not require application to the
Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry for service transaction permission.
HEAD OFFICE: TOKYO BLDG., 2-7-3, MARUNOUCHI, CHIYODA-KU, TOKYO 100-8310, JAPAN
NAGOYA WORKS: 1-14, YADA-MINAMI 5-CHOME, HIGASHI-KU, NAGOYA 461-8670, JAPAN

